by MYB Agency | Jun 24, 2021 | Digital Marketing
Chapter 8 – Google Ads
What Are Google Ads?
In the previous chapters, we came across the different types of SEO and how to optimize your website. In this chapter, we show how you can get maximum mileage from online advertising using Google Ads.
Google Ads, also known as Google Adwords, is Google’s platform for paid online advertising.
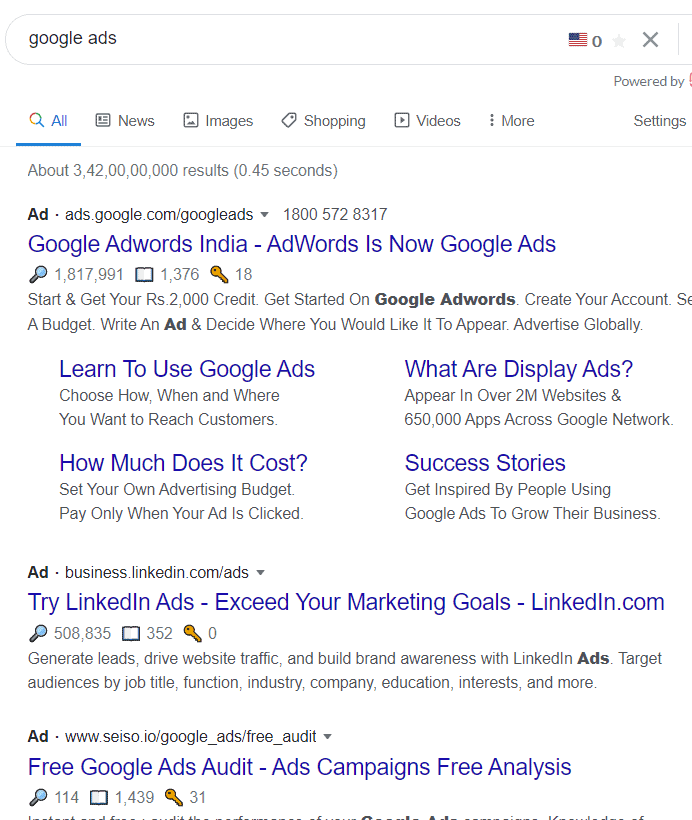
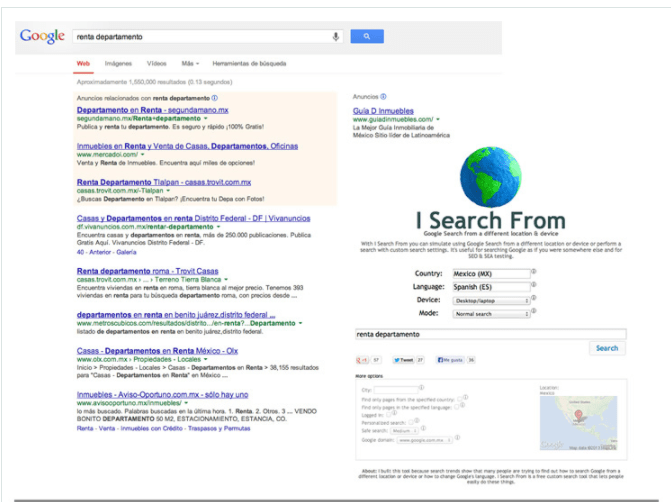
You have probably seen Google Ads in your search results. For instance, if you search “Google Ads” from the Google search bar, the search engine results page (SERP) looks like this:

All the ads are at the beginning of the page and are presented in a similar fashion as organic searches. The only difference is the word “Ad” at the top of the page that you can see above the link. This is what paid online advertising on Google Ads looks like.
These ads are beneficial to advertisers because they occupy prime web real estate: the topmost position on the page. Results that show up in this area get the majority of traffic.
However, purchasing ads on Google will not necessarily give you the top spot in SERPs. This is because there are other factors as well as bidders who are targeting the same keyword/s as you.
Now that you’re aware of what Google Ads are, let’s move on to how ranking works with these paid advertisements.
How Do Google Ads Work?
Google ads work by having different marketers compete against each other for their ad to either be displayed or clicked on. It offers advertisers different strategies which become the basis for payment and how a campaign is measured.
It is possible to pay for ads only when they’re clicked, or when they’re seen, or when a purchase is made. There are many more ways, but the essence is that Google’s structure allows advertisers to only pay for specific interactions between the ad and the person who sees it.
Bidders specify their maximum bid or the maximum amount that they are willing to pay for every successful interaction. Despite the bidding system that is in place, Google does not necessarily award the top spot to the highest bidder. Instead, the system uses Ad Rank to determine where an ad will show if it shows up at all.
Why You Should Care About Ad Rank
What is Ad Rank and what goes into it? Your Ad Rank functions like a score that determines how you rank compared to other advertisers who are targeting the same keyword or spot as you. It is comprised of three things:
- Maximum bid or the maximum amount that you want to pay for every click
- Quality score is determined by several factors, but its three main drivers are the relevance of your keyword, your ad, and landing page to the search query
- The effective use of ad extensions. This is the part of the advertisement that can be seen when users click to expand on your advertisement. By using ad extensions, you can show interested viewers reviews or links to reviews, telephone numbers, links to your website, and any other information that they might use when considering doing business with you.
This is why whenever you submit a bid on Google Ads you should not only consider your bid price but also ensure that you can get a good quality score and are using ad extensions to your advantage.
It is interesting to note, however, that if you rank for a keyword you will not necessarily be charged your maximum bid. Rather, Google assigns different prices to different rankings and keywords. If you manage to rank third out of the four slots assigned to Google Ads, you will not be charged more than the advertiser who ranked second. Similarly, the advertiser who ranked second will not be charged more than the advertiser who ranked first. You then only need to keep paying these assigned amounts to maintain your ranking.
Google Ads offers advertisers three bid types:
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC) refers to the sum you pay to Google when a consumer clicks on your ad.
- Cost-Per-Mile (CPM) refers to the sum you pay to Google for every thousand impressions or every thousand times that your ad is included in Google’s SERPs.
- Cost-Per-Engagement (CPE) refers to the sum you pay to Google when a user performs a specified action on the ad such as signing up for a newsletter or clicking on a certain link.
Google has come up with an innovative and automated way to revolutionize the way we advertise. In the next section, we delve deeper into why advertising on Google is an essential tool for marketers.
Why Advertise on Google?
No doubt one of the questions you’ve had to contend with before reading this chapter was: Why choose online advertising?
- Online advertising provides you with the advantage of displaying your ads and your brand to a very targeted audience whose demographics and criteria you can specify. Because of this targeting capability, the audience you pick can have a much higher chance of buying from you compared to, for instance, using a billboard on the highway which everyone can see, but not everyone finds relevant.
- You can also specify the type of interaction that you are willing to pay for. Remember, Google Ads allows you to bid based on PPC, CPM, or CPE.
- Another distinct advantage of online advertising is it allows you to gain valuable insight into the mileage of your ads. For example, you can track how many people saw your ad versus how many people clicked on it.
- These days, people use different devices for their search queries, and online advertising can help you reach out to them using all these devices.
- Google Ads also helps you reach targeted users at the correct time and place.
Now, let’s take a look at some of the benefits when you advertise online using Google Ads:
Targeted Ads
It’s no big secret that targeted ads perform better than general ads that hope to rope in customers without taking into account their behavior, profiles, and needs. Google’s advertising platform gives you opportunities to customize your ads and the people who see them.
There are targetable elements that you can use to make sure that your advertisement reaches the right audience:
- Optimize your keywords to help the right users find you.
- Fully utilize your ad extension by adding the location of your business and any other relevant information.
- Perform due diligence in identifying the location, language, age group, and any other criteria that will help you reach the ideal audience for your product, service, or business. You can then use Google Ads to target the exact demographic you want.
- Study the behaviors, schedules, and timezones of your desired audience. This gives you a basis for choosing the day, time, and frequency that your ad appears on SERPs.
- Optimize your ads for different devices. Make sure that they display correctly on each device and perform any necessary customizations.
Cost Control
Google Ads allows you to specify the amount of money you want to spend on each ad. There is no minimum amount and you can even specify different amounts on different days.
Measuring Your Progress
You gain valuable market insight by advertising with Google. It makes tracking your progress and your campaign’s success simple by allowing you to see how different users interact with your ad and website.
Google provides you with a wealth of data through its analytics. Learning which campaigns and collaterals are effective will allow you to make more intelligent and strategic decisions when designing your next campaign.
Tools to Help Manage Your Campaigns
When you run an online campaign for your brand, you need to monitor your accounts.
There are times when a single advertiser will need multiple Google Ads accounts. A tool, known as My Client Center, can help you manage all your campaigns from one centralized app while saving time.
If you cannot access the internet and you need to make changes to your ad, you can use the Google Ads Editor, a downloadable app that allows you to manage your accounts offline. Your account information is downloadable, and you can control your campaign online and offline.
Do Google Ads Work?
This is a good and practical question to ask before you start investing in ads on Google. The short answer is yes, Google Ads work. However, you need to know what to do to make it work for you. Let’s take a look at the best practices you should consider.
Best Practices for Google Ads
While Google has made it incredibly easy to have market data, target your ads, and manage your advertising, there’s still a lot for you to do and decide on as a marketer.
Define Your Objectives
The first question you should ask yourself before using Google Ads is: What do I want to accomplish with Google Adwords?
Depending on your type of business and the stage of your business, you may decide to increase sales, increase brand awareness, get leads, etc.
For retailers who have a lot of inventory or a wide product selection, the answer to this question can be a little less straightforward. Not all online sellers know which products will sell well. If you feel uncertain about which product you need to highlight, you can try posting all your products on sites like Google Shopping and Shopify. This will help you identify which products to promote.
Keyword Optimization
Keyword optimization is no less important in search engine advertising. You may wonder why you still need to perform keyword optimization when you are practically paying for your SERP’s ranking, but remember that Google doesn’t just look at your maximum bid amount. Relevance matters too. Make your quality score count by optimizing your ad, landing page, and keyword/s.
Ensure a Seamless Transition From Your Ad
When people click on your ad and move to your landing page, they shouldn’t feel like they might have accidentally clicked on something they didn’t intend to. The transition from your ad to your landing page and website should be seamless. It should be an intuitive user experience that is easy to navigate and provides a consistent look and feel throughout.
Make Sure Your Ad Is Relevant
How many times a day do you get inundated with unwanted marketing emails, pop-up advertisements that clutter your screen, and ads that are simply irrelevant to you? We live in competitive times when marketers come up with new gimmicks, discounts, and deals to lure customers in all the time.
For your ad to work, you need it to stand out and engage users. Here are some best practices to help you create an ad that will help you get noticed and be heard above all the noise:
- Include relevant keywords in the title of your ad
- Add a call to action and use engaging verbs
- Capitalize influential words
- Use correct punctuation. Google likes to see ads with different punctuation marks, but make sure to use them intelligently and not just for ranking as the search engine employs safeguards for the latter.
- Make the most of ad extensions by filling in pertinent business details that allow people to contact and evaluate your business.
Choose the Right Time and Place for Your Ad
We came across this step earlier when we discussed the benefits of Google Ads. Choosing the time when your ad can be seen is an important decision. To help you, Google Adwords provides you with valuable data that can help you identify the habits of your users and the intentions behind your keywords.
Use this data to decide when it would be best to have Google post your ad. You can also target specific locations by selecting a country or smaller areas.
Interestingly, Google Adwords shows you an estimated audience size after you have entered some criteria for your ad. Use the data to help you decide whether or not you would like to further target your audience.
Assess Your ROI
Google Adwords calculates your return on investment (ROI) for every dollar you spend on a campaign. If your ROI is positive, good job! You’re doing something right.
Many factors help you assess ROI such as conversion rate, click rate, cost-per-click, and more.
Test Your Ads
Marketers today have a wealth of tools and resources that they can use to produce effective and engaging ads. You can get a better idea of which ad is most effective by creating multiple ads with the same keywords. Keep all the other factors such as the targeting as well as when the ad is displayed similar to each other.
Launch the ad and look at the data to help you identify which ad gives the best results. Doing so helps you create more effective ads for future campaigns while gaining better insight from your consumers.
Consider Using Banners
Google Adwords helps promote your links, but you can also use Google’s Display Network to increase your visibility through third-party websites.
What is the Display Network?
The Display Network refers to Google’s network of display advertisements that various businesses use. You will recognize these ads as visual banners or small boxes that appear around articles that you are reading. Though not all websites support display ads, a whopping 90% of internet users across two million sites globally are exposed to these ads.
Great! You’re well on your way to adding Google Ads to your arsenal of online marketing tools. Let’s now look at a few key terms that will be useful for you.
Useful Terms for Google Ads
There are many terms associated with Google Ads. Here are a few of the most popular which you will come across.
Ad Group
An ad group is a group of one or more ads that have the same targets. An ad group can share one bid price and keywords, but you can also configure different bids for different keywords. You can organize your ad groups based on certain themes such as the kinds of products or services you offer.
Campaign
A campaign is a set of one or more ad groups that share similar settings such as location targeting, budget, etc. You can use campaigns to further organize your marketing initiatives by product category or the types of services you offer.
Impressions
Impressions refer to the number of times your ad appears on the SERPs.
Mobile Ads
Mobile ads refer to the ads that are visible on mobile devices. Google AdWords include Wireless Application Protocol or WAP mobile ads. Mobile ads are smaller and will direct users to a mobile version of your website.
Split Testing
Split testing refers to the activity of randomly sending incoming website traffic to two different versions of the same page to help pinpoint effective page elements or techniques. The traffic for testing can either be all the visitors of a page, or just a number of your visitors.
Split testing can be used to increase conversion rates, improve ad ranking, minimize bounce rate, increase the number of leads, etc.
Bid Strategy
Your bid strategy should be determined by what you are trying to accomplish with Google Ads. Different bid strategies can be focused on having more clicks, impressions, or conversions. Later in this chapter, we discuss in greater detail when and how to use the different bid strategies available to you.
Destination URL
Destination URL refers to the landing page your ad goes to when clicked. Google allows you to have different landing pages for various ad groups.
Display URL
Display URL refers to the URL that appears in your ad copy. This also gives your visitors an idea of where they will go after clicking on your ad. Keep this as simple as possible to keep potential customers interested and to improve conversions.
Side Ad
The side ad refers to the ad that appears on the right-hand side of SERPs.
Top Ad
The top ad refers to the ad that appears in a box above the organic web results.
Now that you know some of the important terms in Google AdWords, let’s take a closer look at what retargeting in Google Ads means.
Retargeting: A Powerful Tool
Google Ads provides us with a way to market to users who have already visited our website or mobile app. This is a highly desirable group because they have already shown interest in your product or service in the past by interacting with your content.
Retargeting or remarketing means reconnecting with these users through Google Ads.

You can increase sales, drive registrations, and heighten awareness for your brand with remarketing. Remarketing can help your sales campaign by:
Showing Your Ads When Consumers Are Most Likely to Purchase
Google lets you show your ads when users search for your business. You can also have Google display your advertisements to people who have had online interactions with your business even as they search online for your competitors.
Targeting Consumers Based on Their Interaction With You
You can target consumers based on the type of interaction they have had with your online presence. If, for example, a customer added something to their cart, you can have Google Ads send them specific advertisements or messages reminding them to complete their transaction with you.
Providing You With Multi-Device Exposure
From laptops to phones to tablets, consumers today use multiple devices to interact with more than two million websites and mobile apps. Retargeting helps you reach your audience across different devices.
Standard Pricing
Once you’ve secured one of the four coveted ad slots in SERPs, you only need to keep paying a standard price to maintain your rank.
More Customized and Targeted Ads
Hopefully, by the time you use remarketing you will have gained a little more insight into your target market. This will allow you to further target and customize the messaging of your ads based on their needs and situation. Targeted ads are more relevant to your audience and are therefore more effective.
Better Consumer Insight
Retargeted customers provide valuable insight into the behavior of your targeted demographics and how to reach them. Google provides you with analytics so that you can use this data to your advantage. You can see how your ad is progressing, where it appeared, and the price that you paid.
Indeed, remarketing is a powerful and innovative tool that you can use to find your market and achieve your marketing goals. Let’s take a look at some of the different ways you can use remarketing in your Google Ads campaigns.
Make Remarketing Work For You
Since Google Adwords launched remarketing in 2010, the company has evolved to include many ways for us to take advantage of it. Consider which method would be most ideal for your next campaign.
Standard Marketing
Standard Marketing refers to the process of showing your ads to past users while they browse websites on Google’s Display Network.
Dynamic Marketing
A recently released feature, Dynamic Marketing utilizes customized ads that take into account the products and services for which past users have searched. Google uses the behavior of your website visitors to dynamically generate ads that show your price, images that you select, and your copy.
Remarketing Lists
Remarketing Lists provide you with even more targeting capabilities. Using this method entails creating a list that includes rules for when you want certain users to be added to a more targeted list that you can market to in the future. You can also tell Google how long members should stay on that list.
Video Remarketing
Video Remarketing refers to your retargeted audiences to whom Google shows your video ads.
Customer Match Remarketing
You can use Customer Match to re-engage with visitors across Google’s search function, shopping tab, Gmail, YouTube, and Display Network. Customer match uses information that visitors previously shared with you to match them up with relevant ads from the aforementioned platforms.
Here are some ways you can use Customer Match Remarketing to reach your audience on these platforms:
- For Gmail, you can show your customers targeted ads above their inbox
- On YouTube, you can identify new users who have similarities to your most high-value customers.
- You can use the Display Network to show personalized ads to retargeted visitors or find new customers by displaying your ads to visitors who share similarities with your remarketed visitors.
After exploring different remarketing techniques on Google, let’s see which type of Google campaign will work best for you.
Types of Google Ads Campaigns
Different objectives entail different campaign types. Google offers several types of campaigns to help you achieve your goals. There are seven kinds of ad campaigns that you can use. Find out which one is most relevant to your objectives.
Search Campaign
What it is: A Search Campaign shows your products and website to users who are searching for similar products online.
Why choose it: It drives search traffic to your website while boosting your reach. This is an easy setup to implement with highly targeted results.
Display Campaign
What it is: A Display Campaign relies on visually strong and compelling ads. It uses Google’s Display Network to attract customers.
Why choose it: People use Google to look for something, but they don’t stay there. This type of campaign allows you to display your ad on websites other than Google while remaining targeted and having access to Google’s analytics.
Video Campaign
What it is: A Video Campaign lets you show a video of your ad on YouTube.
Why choose it: When used correctly, videos can be a much more engaging format for users than web layouts and copy. If you choose to go with a Video Campaign, Google provides you with several ways to integrate your video ads on YouTube. You may want to check out this video where they explain how its different features enable potential customers to interact with you on YouTube.
Shopping Campaign
What it is: A Shopping Campaign promotes your product by displaying your product along with detailed information before clicking on your ad. Ads under this category show a photo of the item for sale, the name of the product, its price, your store name, and more.
Why choose it: A Shopping Campaign creates visually engaging product listings for you. It can help boost sales, add traffic to your site, and help you identify stronger leads.
App Campaign
What it is: Google provides you with tailored ads to promote your apps.
Why choose it: Google displays ads for your app on its owned networks and platforms such as the Display Network, Google Play, Google Search, and YouTube. You only have to supply Google with photos, text, and some information on your targeted audience. It will automatically find the optimal combination that produces the best results and push that ad more.
Local Campaign
What it is: Local Campaigns utilize the same Google platforms and networks to promote your ads. The only difference is that it has a more local focus; ads are geared towards helping potential customers make contact with local businesses.
Why choose it: The Local Campaign gives you visibility on Google Search, Maps, YouTube, and its Display Network. Similar to the app campaign, Google takes care of creating several versions of your ad based on the assets you submit and uses the version that performs the best.
Smart Campaign
What it is: First, a little context: Smart Campaigns were developed as an offshoot of Google Adwords. When Adwords was first released in the year 2000 many users found its functionalities and interface overwhelming. To encourage more people to use Adwords, Google released a simplified version called Adwords Express in 2011. Today, this is known as Smart Campaign.
In a nutshell, a Smart Campaign is a text-based version of your ad that contains the following standard elements: a headline, a description, your website URL, automatically generated site links, a map pin, address, and phone number.
Why choose it: Because of the simplicity in execution, a Smart Campaign is an excellent option for small businesses with modest budgets that don’t have a technical team behind them. You still get access to Google’s network and platforms, but you’ll have a relatively easier time setting up and running your campaign.
So far, we’ve come to understand a great deal about Google Ads such as what they are, how they add value, best practices to adopt, and the different ways you can use them. Let’s get started with the exciting part: creating your first Google Ad.
How to Create Google Ads
Google Ads provides an easy step-by-step process to help you launch a campaign that matches your objectives. Follow along with us as we take you through it.
Signing Up and Creating Your First Campaign
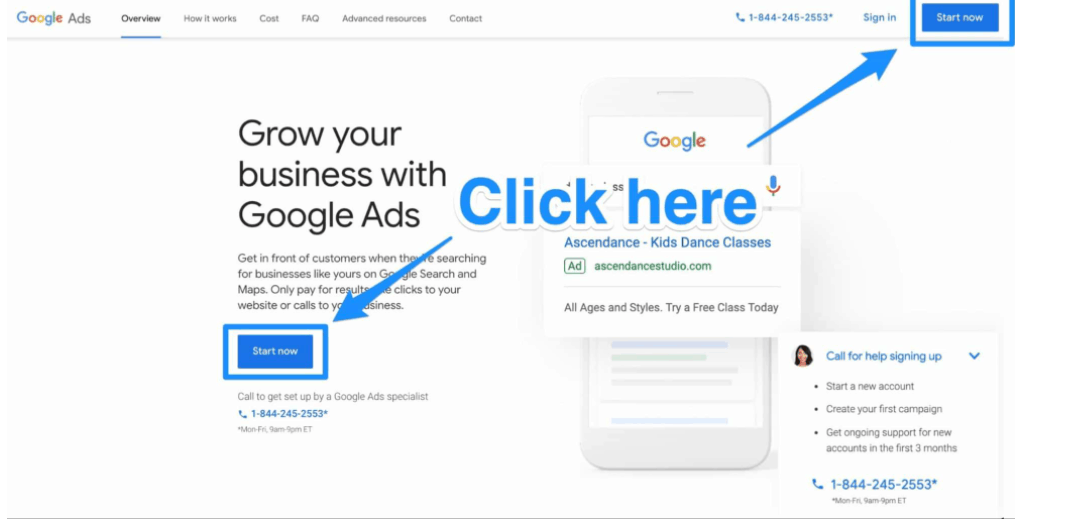
Creating a Google Ads account is the first step to ad creation.
- To do this, go to Google Ads and click on the button to get started.

- After signing up for an account, Google takes you to your account’s dashboard. Click on the plus sign with the words “New Campaign.”
- Remember how we mentioned that you need to identify the objective for your campaign? That step comes into play here when you choose your campaign goal.

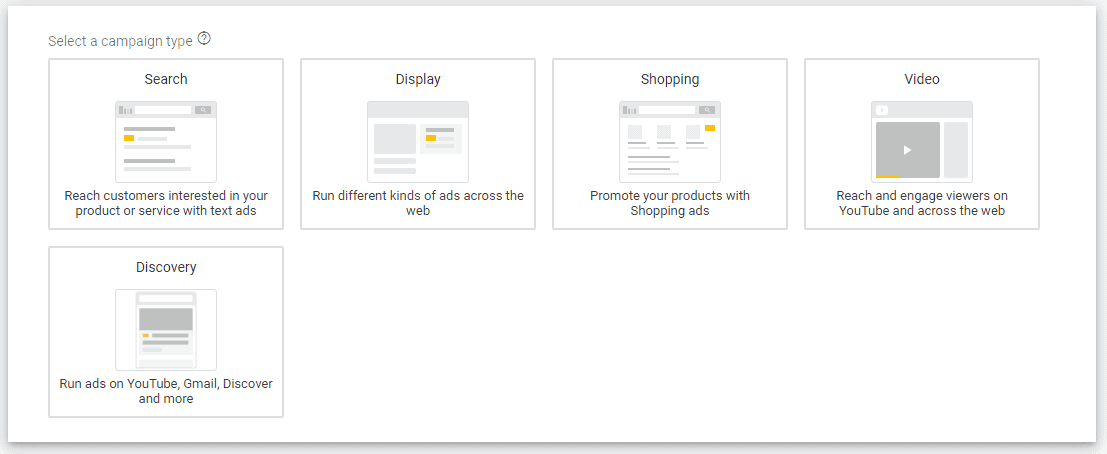
Google then presents you with relevant campaign types based on the goal you choose. You will see these types immediately below the objectives.
These are the campaign types available if you choose “Website traffic” as your goal:

If you feel confident about your marketing and Google Ads skills, you can also choose “Create a campaign without a goal’s guidance” so that all campaign types become available to you.
Your First Campaign: An Example
From here on out, the process varies as each campaign type requires different information from you, the advertiser.
Worry not, however, because if you went through this guide carefully then you should be able to navigate your way to a complete ad before you know it. Google also provides some hints for you to follow if it is your first time.
To give you a better idea of what it’s like to set up a campaign, we’ll take you through an example of a common campaign type: a Search Campaign to increase website traffic.
After choosing the corresponding options in Google Ads (Website traffic<Search), enter your business website’s URL.

You’ll be taken to the next page. The next part is a four-step process:
- Select campaign settings. In this part, Google asks you to provide a name for your campaign as well as general information such as:
- The Google networks you want to use for your campaign (i.e., search network or Display Network?)
- The start and end date of your campaign
- Which days and at what times you want your ad shown
- Locations and languages you want to target
- Specific audiences for the campaign
- Your budget
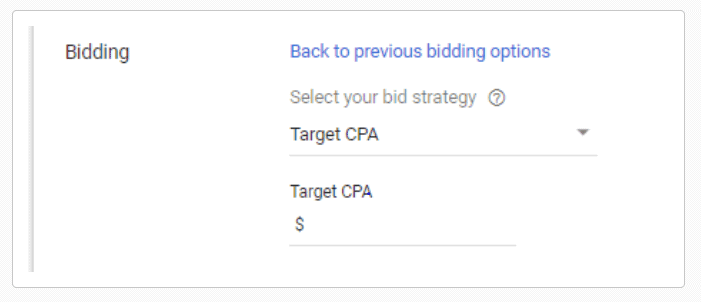
- Bidding or the basis upon which Google bills you (In this instance, the available options are clicks, other optimization options, and impression share)
- Ad extensions (remember not to neglect this part as it will affect your bidding and ad ranking!)

You can further customize these settings by simply clicking to expand each menu setting.
A Word on Audience Size
Your first instinct here might be to get as many people as possible to see your ad and select a huge audience. In reality, smaller, more carefully thought out audiences can produce better results and are more cost-effective. Carefully plan out your targeted audience.
A more focused and specific audience will allow you to tailor your ad to them so that it can be more relevant to their needs and the messages that they are inclined to respond to.
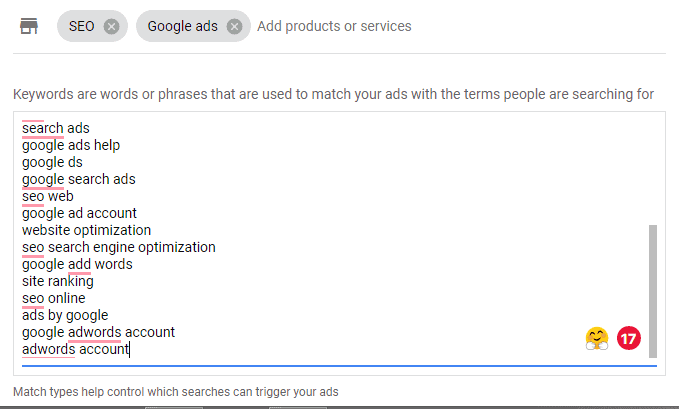
- Set up ad groups. Give your ad group a name and enter the keywords you have identified. Based on your entries, you can have Google add suggested keywords.

- Create ads. Use this section to:
- Define your final URL or landing page
- Tell Google what your display URL should be
- Give Google headline options for your ad
- Provide text description options for your ad. This is the text that is shown immediately below your headline.
- Experiment with different headlines. Google helps you come up with a strong ad by rating your headlines as you type. A strong ad for Google means providing a fair number of headline options, using keywords in your headlines, and unique headlines and descriptions.
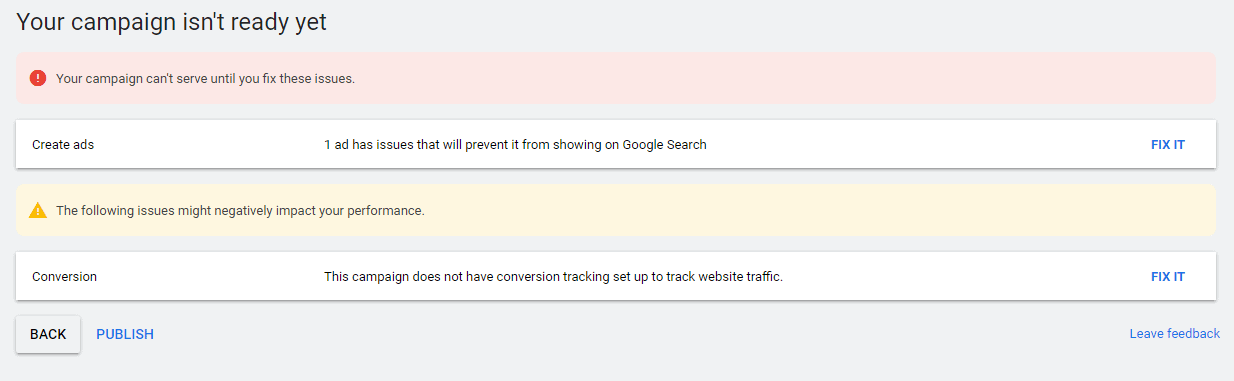
- Review. In the final step, Google asks you to review your ad and sign off on it. It will also notify you if any issues are preventing your ad from being included in search results and if you have missed any steps that can adversely affect your ad’s performance. Review your ad and fix all issues before publishing.

Even if you are linking an existing Google account that has your payment information to your Google Ads account, Google Ads requires you to enter your billing information on its platform.
Congratulations on making your first ad with Google!
Now that you’ve discovered how easy and intuitive Google Ads is, why don’t we become better acquainted with the different bidding strategies?
Google Ads Bidding Strategies
Choosing the right bidding strategy for your ad is essential since selecting the wrong one can be unnecessarily expensive and can derail your campaign. Let’s get to know the strategies available to you.
Target Cost-Per-Action
Target Cost-Per-Action (CPA) is an automated bid strategy that’s designed to get you as many conversions as possible. The price per conversion will be the price you set or lower.
What is conversion? Conversion here refers to whenever a user performs an action that you define when setting up your campaign. Some examples of conversions are sales, leads, and downloads.
If you were to launch an App Campaign, your target CPA sets how much you pay every time Google successfully gets a user to install your app. Setting your CPA boils down to one question: How much are you willing to pay per conversion? If you are a retailer and your product is priced at $70, you cannot set your CPA at $70 as it will mean taking a loss.
If your campaign’s primary objective is conversions, CPA is your go-to bidding strategy.

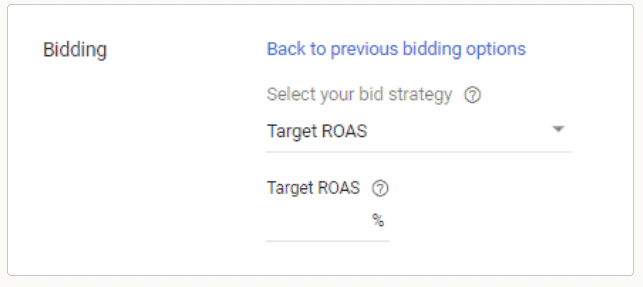
Target Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
Return on Ad Spend is a marketing metric that allows marketers to calculate your revenue for every dollar spent on advertising. It is similar to return on investment. While this can seem more complicated at first, it provides you with a more accurate picture of your campaign’s success since it takes into account the value of each conversion.
The CPA bidding strategy lets you account for volume since it tracks your spending per conversion. ROAS, on the other hand, factors in the value of that conversion.
Let’s say that you run two different ads and set your price at $20. One ad group might have generated a conversion worth $100 through your website while in the second ad group you can see that another user spent $50. If you were to use CPA, they would both be worth the same amount to you. However, if you use the ROAS formula to calculate your return on ad spend (return on ad spend = conversion value ÷ cost), you would be able to see that the first ad group yielded better results.
The higher the ROAS the better. You should generally aim for a ROAS of 3-4 or higher.
To measure ROAS and have this metric in Google Ads, you will need to assign conversion values to conversion actions. If you are part of an e-commerce business, many platforms have made this a straightforward process. If you are unsure of what value to assign, you can review your top-performing campaign to provide you with a realistic target.

An Update on Target CPA and Target ROAS
Google announced that Target CPA and Target ROAS are being retired as of April 2021. Like most changes that Google has rolled out, we expect that the move will be gradual. However, if you are using these campaigns you may want to start preparing for the change.
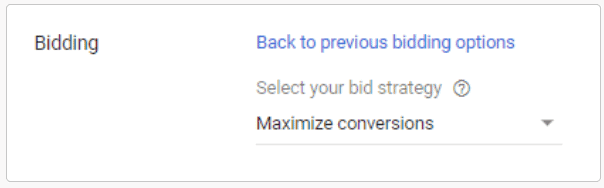
Maximize Conversions
If you are looking for a simple bidding strategy, you may want to look into Maximize Conversions. With this bidding strategy, you need only set your maximum daily budget for your ad campaign. There are no keywords that you need to specify for Maximize Conversions. Google just runs its algorithm and selects a cost-per-click bid based on your campaign goal.
As you might guess from the name, this strategy is designed to get you as many conversions as possible using your daily budget regardless of how your conversion worked out for you. If profitability is not an issue for you, then by all means consider Maximize Conversions.
A Word About Average Daily Budget
One of the unique aspects of Maximize Conversions is its use of an average daily budget. Unlike a maximum bid amount where the rate you’re charged never goes beyond your specified number, with the average daily budget you can find yourself being charged higher on certain days than the amount you entered.
In average daily budget, Google keeps track of your monthly spend. On some days your daily spend can be lower, but there can be days where Google charges you higher for as long as your monthly spend remains the same. Google can charge you up to twice your average daily budget.
You can compute your average daily budget by first determining how much you would like to spend in a month, then dividing that figure by 30.4, the average number of days in a month.
Here it is expressed as a formula:
Average daily budget = Monthly ad spend
30.4

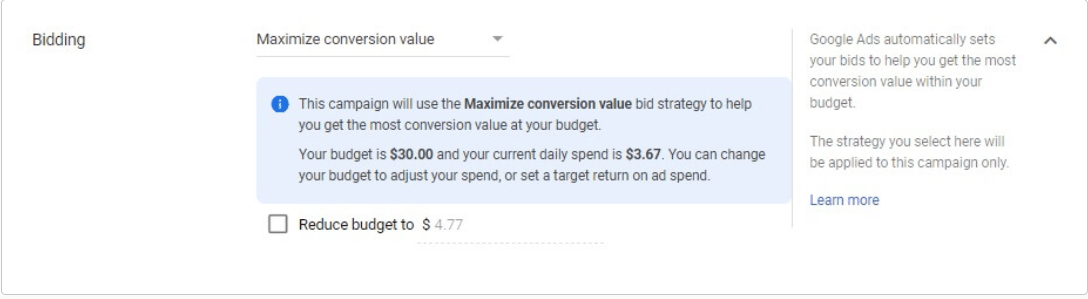
Maximize Conversion Value
Maximize Conversion Value is the most recently added bidding strategy. The mechanics of this strategy are similar to Target ROAS. However, unlike the Maximize Conversions strategy, Maximize Conversions Value is not focused on conversions alone. You can tell Google which aspects you want it to focus on (e.g., profit margin, revenue) and it will make real-time adjustments to bids to help you meet that goal. Google uses data from your past campaigns as well as contextual signals from search engine users in adjusting your bid.
When using this strategy, Google tends to use up your daily budget. We recommend that you double-check the amount you entered to make sure that it is an amount you are willing to spend daily.

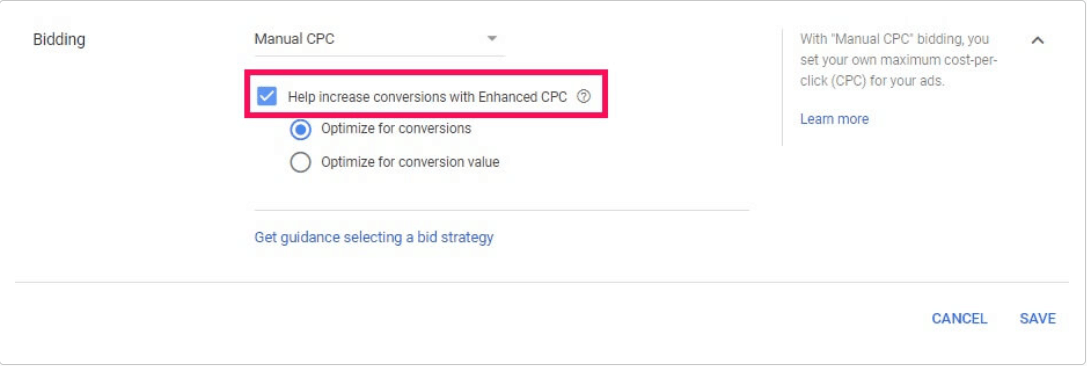
Enhanced Cost Per Click (ECPC)
You know what cost per click means. This bidding strategy takes it one step further. You choose the cost per click, but Google’s algorithm optimizes it.
Google can increase or decrease your bidding amount for clicks that are more likely to lead to a conversion or sale on your website. With Target ROAS and Target CPA you have a set price for your ROAS targets and CPA targets, but with ECPC Google does its best to keep your average CPC spend below your maximum bid amount.
While ECPC may sound like a simple bidding strategy, keep in mind that you do not get the same level of control over your ad spend as you do with other bidding methods. If you’re new to Google Ads it would be wise to try ECPC on a smaller scale first before doing a full rollout.

Maximize Clicks
Maximize Clicks is a lot like Maximize Conversions, but the focus is on clicks instead. Google will work on getting as many clicks for you using your daily budget. As you can probably tell by now, this is a great option if your goal is to get more traffic to your website to build brand awareness or to expand your potential customer base.
One issue that you may run into with this strategy is not getting quality or relevant traffic.
Another is your CPC. You may notice that there are days when Google uses higher CPC bids to use up your daily budget so keep an eye on this.

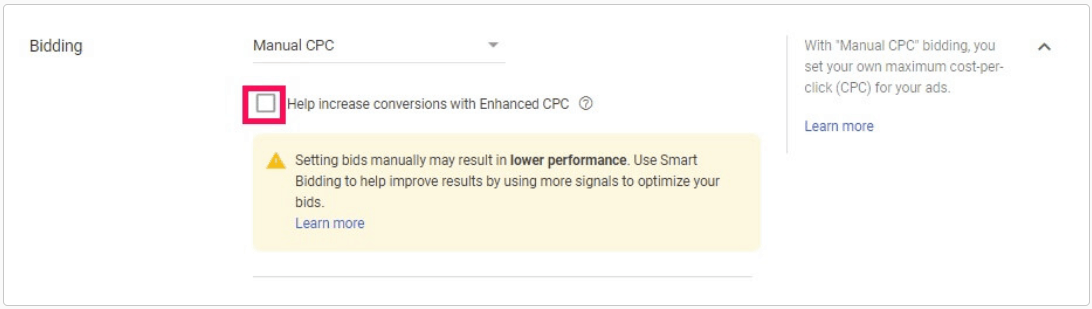
Manual CPC Bidding
If you have no time restraints and you can monitor your account pretty often, you can try Manual CPC Bidding. This is the easiest Google Ads strategy to grasp. You set a price for keywords and you keep using that bid until you change it. You can customize different ad groups and keywords so that they have their own bid amounts.
If you’re new to Google Ads, Manual CPC Bidding can be a good place to start and get your feet wet. However, you may find that it quickly becomes a time-consuming and tedious task that eventually leads you to look to one of Google’s automated strategies.

Cost Per Thousand Impressions (CPM)
Cost Per Thousand Impressions is beneficial if you are looking solely at impressions or the number of times your ad is displayed. Your ad will not be available within Google’s search networks as CPM restricts itself to the Display Network and YouTube Ads.
If your aim is brand awareness, CPM can be a viable manual bidding strategy. However, note how Google qualifies an impression: as long as 50% of your ad is on the screen for at least one second and at least two seconds if it is a video ad. It is thus important to monitor this strategy to ensure that your ad shows up on relevant sites only and that viewers do not get overwhelmed by its frequency.
Cost-Per-View (CPV) Bidding
Cost-Per-View Bidding is Google’s way of measuring and charging you for campaigns that are anchored on a video ad. In CPV bidding, Google counts the following as a “view” for your ad:
- When a user watches at least 30 seconds of your ad, or for the duration of your ad if it’s less than 30 seconds
- When a user clicks on a companion banner, YouTube card, or a call-to-action overlay
With CPV you can be charged your maximum CPV bid or lower.
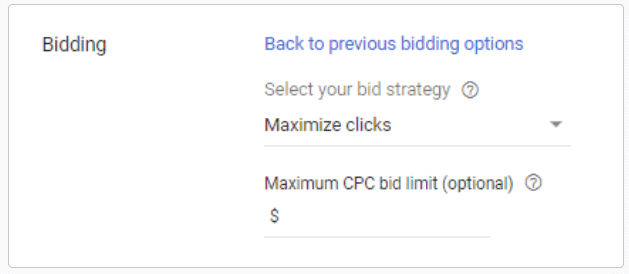
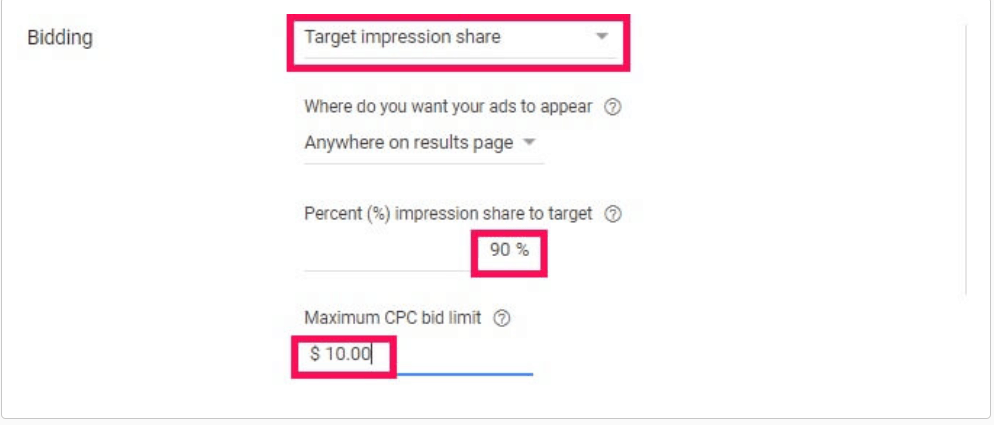
Target Impression Share Bidding
Target Impression Share bidding is a strategy you’ll want to use for brand awareness that takes into account the total number of impressions that are available for your brand.
What is impression share? Impression share is the percentage of impressions that you received from your ad in comparison to the total impressions that you could have received or been eligible to receive.
Target Impression Share gives you a choice on where your ad appears. You can either tell Google to put your ad at the top of the page, at the top of SERPs or anywhere on the SERPs. After doing so, you then tell Google the percentage of impressions that you want to appear in.
You should use a maximum CPC amount for this type of strategy to ensure that you don’t end up paying too much for a single impression. Google Ads will warn you against setting this amount too low, but if you’re new to Google Ads it is better to start out low and see how it goes. After all, you can always increase it later.

We hope that our section on bidding strategies has you thinking about the different ways you can run campaigns on Google Ads. It will take some time before you become fully proficient in using it. To help you get there faster, let’s go through common mistakes you’ll want to avoid.
Mistakes to Avoid
Some mistakes are common to beginners. We share them with you here so you can steer clear of them.
Review And Update Conversion Tags
When you use Google Ads for conversions, you receive a tracking conversion tag that you attach to your landing page. This tag captures valuable data on how different users interact with your landing page which is then turned into a report that you can use to improve your campaign.
Old and outdated tags add a lot of noise to the data you’re viewing. They make it harder to drill down into current and more relevant data. Check the conversion section of your Google Ads account periodically to see if there are old data and tags that you don’t need anymore. Remove the unnecessary ones. You should do this at least quarterly to cut down on noise and make sure that you’re being fed only the data that you need.
Check Your Geotargeting
Did you know that even after you’ve entered your geotargeting preferences Google can still show your ad to users outside those locations? Click to expand the menu in the locations section under “Targeting and audiences” and you’ll see that the following choice has been selected by default: “Presence or interest: People in, regularly in, or who’ve shown interest in your targeted locations.”
If you want to pay for promotion that only targets the people in the locations you’ve chosen, choose instead: “Presence: People in or regularly in your targeted locations.”
With Google Ads, it pays to be thorough.
Fine-Tune Your Ad Schedule
After using Google Ads for some time, you will have valuable data on your ad’s performance such as the schedules when you had the most conversions or perhaps the time of day when a lot of people browsed through your mobile site. We encourage you to make the most out of this data and use it to tweak your campaigns so that you can allocate more resources to these times and schedules when your campaign performs its best.
Tighten Your Bids
Just as you fine-tuned your ad schedule, you should also review your campaign periodically for a deeper insight into where your market is and its behaviors. Looking at your data you may find that your ad is more successful in certain cities or discover that you have more conversions on mobile phones.
Sure, you could use bid modifiers to make changes to your campaign, but it has its limitations. It isn’t nearly as effective as looking into your data, analyzing it, and making appropriate changes to help tighten your bid for a more effective campaign.
Be Open to Different Bid Strategies
We’ve seen advertisers stubbornly stick to one bidding strategy because it’s the one that they are familiar with. This might save you some time in terms of learning a new strategy, but it can cost you more than you think in the long run.
Keep exploring and experimenting with other bidding strategies to see which one is the best for your ad campaign.
Leverage Custom Affinity Audiences
You can target users by location and language, but did you know that you can also target them by interest? Use the Custom Affinity Audience (CAA) feature on Google Ads by going to the audience section of the menu. Go to “What their interests and habits are” and towards the bottom you’ll find an option to create a Custom Affinity Audience.
Targeting by location and language is necessary, but it can also be too broad. To make CAA work for you, think of the websites, apps, places, and interests of your market. You can enter these into Google as CAA and it will analyze the information you’ve given to find the audience you want to reach.
Manage Ad Extensions
Just because you have an ad extension associated with your account, ad group, or campaign doesn’t mean that Google will display it along with your ad. What makes Google show some ad extensions and neglect others?
- Ad Rank. Google has a minimum Ad Rank requirement to show ad extensions.
- Your position on the SERP. Ads positioned higher up get prioritized for ad extensions. If the ad above yours doesn’t have an ad extension, you won’t get one either. Similarly, when Google shows you combinations of extensions you’ve enabled, it will not show you combinations that can have a higher click-through rate than an ad with a higher position.
If you want your ad extension to show, look into raising your bid or increasing the quality of your ad, or both.
It’s easy to think that your task ends after hitting the “Publish” button on your ad. However, it’s helpful to see your first ad as a stepping stone for stronger and more relevant ads in the future.
Because the data that your ad generates is important, let’s turn our attention to how we can perform basic actions in Google Ads’ reporting feature.
Using Google Ads Reports
After submitting your first ad, you’ll want to look at the information that Google generates for you. In this section, we teach you how to access them.
When you begin your ad campaign with Google Ads it comes with automatically generated reports based on your data. These reports answer specific questions and can be edited according to your needs.
To access these reports:
- Sign in to your Google Ads account.
- Click on the reporting icon on the upper right side. This will show you a list of predefined reports.
- Choose and open one with the Report Editor.
- From here you can edit the report and save it.
If you want to view a report created by you, you will find the option to do so by clicking on the three dots under the “Reports” section.
Advertisers and business owners have never had as much control over their ads as they do now. If you have a product or service to promote or a brand that you want recognized, learn Google Ads. While any new tool or endeavor takes time in the beginning, the long-term returns are worth it.

by MYB Agency | Jun 23, 2021 | Digital Marketing
Video SEO – Ranking your videos
What Is Video SEO?
Have you tried to make the videos on your website more appealing by minimizing your video’s length, adding catchy titles, and even hiring a professional for production? If yes, did it help you get more views and improve your ranking? If your answer is no, you have come to the right place.
Video SEO is different from regular SEO. It refers to the optimization of videos on your website to help get views from Google and increase your organic traffic. You achieve video optimization when your videos generate a return on investment (ROI).

The first thing you need to do is to decide on your goals for your videos.
Define Your Video SEO Goals
Videos are an effective and exciting way to get organic traffic to your website. However, you need to consider a video strategy that fits in with your regular SEO strategies. Why is it necessary to define your video goals, you ask? If you do not establish your goals, you might end up spending a large amount of money on a video that is not even appropriate for your website.
Some website owners experience what is known as FOMO (fear of missing out) when they see other websites including videos. They also start producing a video for their website without even considering what they require from the video.
You need to ask yourself: Do I want videos for high-quality traffic, conversion, or simple organic traffic? When you set your video goals accordingly, you are more likely to find the right audience for your videos.
If you look at your video goals from an SEO point of view, there are two goals you can have. It can either be to build links or increase conversions. Let us understand how building links and increasing social shares can be beneficial.
Building Links and Increasing Social Shares for video seo
High-quality videos can generate links like no other element. It can help you link to the top domains provided you have relevant videos.
It can be tough to get these links as there is so much video content online. You require an outstanding video with an exceptional outreach strategy that positions it for backlinking from other websites.
Relevance is again a crucial factor when it comes to choosing a website you want to link from.
What do you think is the defining factor of your video? How is it any different from the ones that are already out there? These are the questions you need to answer to help determine where your videos currently stand.
Your videos need content that engages the audience and compels them to share it through social media platforms.
Moz Whiteboard Friday
As mentioned above, you need an out-of-the-box element for your video. This element will help you attract high-quality links to your website.
Try making your videos educational. One of the examples of these videos is Moz Whiteboard Friday.
Popularly known as Moz Whiteboard Friday, Moz posts a whiteboard-style video every Friday. A whiteboard-style animation refers to the static images drawn on the board while a narrator speaks in the background explaining the drawing.
Moz Whiteboard Friday attracts numerous links and social shares which increases their organic traffic. Moz Whiteboard Friday is an excellent example of how building links is easier by releasing engaging video content.
I must remind you, however, that you need to be sure of your video goals first. Putting all your efforts into outreach strategies and paying zero attention to the value your video provides will not help you achieve your goal.
Pro Tip: Try posting videos directly on your website rather than using video platforms like YouTube or Vimeo. This will help drive traffic to your website since viewers will have to share your website’s link when they share your videos. If you plan on posting your videos on video platforms, remember to link them back to your main webpage.
Increase Conversions for video seo
The primary aim of any VIDEO SEO process is to improve your ranking which in turn helps with sales and conversions.
However, increasing conversions is more than a singular process. First of all, you need to attract people to your website. Secondly, you must optimize the website for people to be paying clients.
Videos are an excellent tool for conversion as they can help people stay engaged with your website. This element is especially beneficial when you add it to your website’s landing page.
Adding videos to your landing page is one of the primary ways to increase conversions. Another way to do this is through rich snippets.
But first, let us look at how videos on landing pages help with conversions.
Video SEO for Landing Page
You only have just a few seconds to engage a visitor through your website. This necessitates an optimized landing page. If you only optimize the written content on your landing page, it may not be enough for visitors. You require their attention, and videos are an engaging way to get that.
When you visit any website’s landing page and spend time looking at a video relevant to the business, you want to know more about it.
That is how video SEO works on a landing page. Once viewers see a convincing video about your brand, they are more likely to become paying clients. Product videos and explanatory videos are two ways to reel customers in.
Product Videos
If you are a retailer wanting to increase conversions, product videos are the ultimate solution. People buying products online feel a lot more confident if they watch the product video first.
Your product video should not contain unnecessary details. It should be concise and relevant.
Here is an example from Zappos and their product video for Levi’s jeans for women. Econsultancy reported that after Zappos introduced product videos, their sales increased from 6% to 30%.

Explanatory Videos
If your brand deals with services, you can use explanatory videos for your conversions. There is no exact formula to create these videos as it depends on what kind of services you provide.
However, if you produce an introductory video of your brand, your conversions are more likely to increase. This type of video can help describe why your services are top-notch while also providing a preview of your services.
Dropbox did just this by adding videos to their homepage which increased their conversion rate by 10%.
After having established the importance and potential of video SEO, let us look at other ways you can increase conversions with video SEO:
- Video SEO Through Rich Snippets
Google customarily provides a short description of your website below each search result. These are known as normal snippets. When Google provides additional information taken from structured data in your page’s HTML, these are rich snippets. Some common types of rich snippets include recipes, reviews, and events.
Sometimes, people refer to the rich snippets before they visit the landing page of a website. Google has recently increased the use of rich snippets in their search results. You can take a look below for a reference to a video that has a rich snippet in the SERP.
Google displays information about your video and helps the user know that they can watch the video once they click on the link. Since users can already see your video snippet, they are more likely to visit your website. This increased traffic can improve your conversions eventually.
The thumbnail of your video is visible to the users along with the duration. It is a good practice to optimize your thumbnail by ensuring that it matches your web page’s context.

A crucial question arises: How do you use rich snippets for Video SEO?
The fundamental rule in using rich snippets for video SEO is to host the video on your website. If you work on WordPress, you can use YouTube through the Yoast plugin.
Once you have posted the video on your website, you can inform Google by adding schema codes and submitting an XML sitemap on Google Search Console.
It might seem like a tedious task, but once you start doing it regularly, you will get the hang of it. If you are ranking for high-volume keywords already, these rich snippets work like a bonus.
By now, you know the basics of video SEO. Now let us look at how you can perform keyword research for your video.
Video SEO Keyword Research
Keyword research for video seo is different from the keyword research methods we have previously taught you for written content.
You’ll need to perform different keyword research for your videos since the views you get for your videos come from YouTube searches and not search engines. Though it is essential to optimize your videos for both YouTube and Google, YouTube has the upper hand.
Another reason why a separate search is necessary is that people use Google and YouTube differently. For instance, a keyword like “health insurance” may get millions of hits on Google, but it may only have a few hundred hits on YouTube.
The keyword phrase “adorable dogs” may get millions of hits on YouTube, but it may not have as many hits on Google. Hence, you’ll need to do separate keyword research for video SEO.

In the following section, we look at some research techniques for video keywords.
Using YouTube Suggestions for video seo
This is similar to Google’s suggestions. When you add a keyword on YouTube’s search bar, you get a list of options. These keywords are potential video keywords.

Using TubeBuddy Tags for your video SEO
If you want to know what video tags your competitors are using, this extension is your answer.

You need to install the extension on your Chrome browser and visit your competitor’s YouTube page.

Look at the tags tab. The numbers in green boxes indicate how specific keywords rank in YouTube.

Imagine this scenario: you come across a low-quality video (relevant to your brand) with a keyword that ranks on YouTube. Why not produce a high-quality fully-optimized video using the same keyword to outrank the previous one?
Using VidlQ Keyword Search for video seo
You can use this tool to search for keywords for free, but of course, premium paying members get additional benefits.

Within seconds of signing up, you get many keywords and phrases. Add your main keyword on an SEO search bar, and voila! You have all the relevant keywords and phrases for your video SEO.


VidlQ also shows the information on high-volume keywords that have low competition.
Using YT Cockpit for video seo
This tool works specifically for YouTube keyword research. You need to add your seed keyword into the search bar of this tool. The tool will then display a list of keywords and phrases with each keywords’ metrics.

If you come across the monthly searches column in YT Cockpit, it refers to Google searches, not YouTube searches.

An important element of this tool is the competitor analysis it provides.

This tool gives you a list of all the highly successful videos for the selected keyword. If there are many successful videos for a particular keyword, you can choose to work with another relevant keyword.
Using YouTube Studio Stats for video seo
Since this tool shows keywords that you have already ranked for, your channel needs to have at least some traction for this tool to be beneficial. 
This tool offers you the best keywords for your videos. You can take a look at them via the YouTube Studio dashboard. You can find an analytics option that leads you to reach viewers.

Select the traffic source as YouTube searches and you can see your already ranked keyword list.

Once you see this list, you can use it in one of two ways:
- Optimize an existing video around those keywords
- Create a new video using those keywords
Now that you know how to look for keywords for your videos, let’s move on with learning how to create top-ranking, engaging videos.
Creating Engaging Videos
Have you ever started watching a YouTube video that you felt like turning off after the first few seconds? On the other hand, have you ever found yourself enjoying a video so much that you not only watched it to the last second, but watched it again, and shared it with your friends?
Both videos in the above scenario may have entailed a lot of hard work from their producers, but only one of those videos will have desirable results.
What makes one video better than the other? I’m glad you asked. There are several metrics that YouTube uses to rank your video:
Watch Time for your video SEO
The Total Watch Time is the most crucial ranking factor on YouTube. It refers to the complete duration of your video.
You can find this metric on YouTube studio.

You can optimize your watch time by creating long videos. Consider this scenario: You create two videos for your channel. The first video is 30 minutes long while the second video is ten minutes long. If people watch 40% of each of your videos, the first video will have three times the watch time that the second, shorter video will have.
This is the explanation behind the idea that longer videos are more likely to have a higher ranking on YouTube.

Increase Audience Retention
Audience retention is another ranking factor for YouTube videos and improves video SEO output. It refers to the total amount of time that audiences watch your video.

If you can improve your video’s audience retention, you can rank higher on YouTube.
- Pay attention to the first 10 to 15 seconds of your video. If you cannot engage someone within that 10 to 15-second timeframe, they will not watch the rest of the video.

- In your YouTube studio stats, check the audience retention reports for your videos. You can see at which points audience retention peaked and dropped in your video.

- Try adding pattern interrupts. Pattern interrupts refer to the moments in your video when you change things up a little. It is an element designed to help break the monotony and keep things interesting.
We will look at this metric in more detail in the YouTube SEO section.
Session Watch Time
Session watch time refers to how long a person spends on YouTube after watching your video. YouTube ranks videos with a higher session watch time. Unfortunately, there is no possible way to measure your session watch time.
There are, however, ways to optimize it:
- Create a playlist. If the audience selects a video from your playlist, your session watch time increases.

- Links at the end of the video give the viewers a chance to visit your channel and improve your session watch time. Try YouTube’s End Screen feature to add this feature to your videos.

User Engagement
If viewers watch your videos without liking, sharing, subscribing, or commenting on them, it does not help user engagement. YouTube uses the share, like, subscribe and comment functions to measure if viewers actively engage with your videos.
There are ways to improve your videos’ user engagement:
- Ask your viewers to comment on the video.
- Add a subscribe call-to-action to your video.

- Reply to the comments you receive on your video.

Now that you know how to create and determine what an engaging video is, let’s look at some ways you can optimize it for video SEO.
Ways to Optimize Your Videos for Search
The optimization of your videos is as important as optimizing your written content. The video optimization process also includes video keyword optimization.
Try these steps for optimization for video seo
Select the Correct Video Hosting Platform
Selecting the right video hosting platform for your video entails knowing the answer to the first question in this chapter: Why do you want video SEO? What are you trying to achieve? Once you can answer this question, you can proceed with choosing the right video hosting platform.

YouTube and Vimeo are good choices if your goal is brand awareness.
Include a Video Transcript
If you come across a video that has real-time captions, then it has a video transcript. When you add video transcripts to your videos, you make them accessible to a broader audience. It also helps bot crawlers find your videos more easily with the additional information provided by the transcript.
Create an Appealing Thumbnail Image
Whenever you browse through videos, you are scrolling through thumbnail images that represent them. This matters because they are the first encounters that potential viewers will have with your video. Thumbnail images are a big factor in helping visitors decide whether or not to click on your video file.
You should therefore strive for a thumbnail image that is appealing and relevant. If your video is about DIY face masks, your thumbnail picture should depict that. Any random out-of-place photograph will not compel users to click on your video.

Choose the Right Title and Description for Your Video
When you write a catchy title and a meta description for your video, you are more likely to get views. Remember to include the targeted keyword in your title.

You should also take the time to research how to make titles and descriptions clickable.
Other Content Should Be Relevant to Your Video
Your webpage is more than just your video. It has other elements too. Focus on optimizing other components. Use these elements to explain the relevance of your video.
Gaining organic traffic is a tedious process, but worth it if you optimize all the components of your website.

Put the Video You Want to Rank First
This step applies to a webpage that has multiple videos. Google usually indexes only the first video on a webpage. Bot crawlers stop indexing after the first video. Hence, you must put the video you want to rank first on your webpage.

Put Focus on Your Ranking Video
This step is an extension of the previous step. You should avoid adding lengthy information and adding other unnecessary elements to your video.
It’s worth repeating that you should place the video you want to rank towards the top of your website. People don’t like scrolling a lot just to find the main content.
Do Not Put the Same Video on Multiple Pages
Embedding the same video on different pages of your website only creates unnecessary competition for yourself.
It is likewise illogical to duplicate the same elements that you have on a ranking page to other pages on your website.
Do not do either of these things.
Explore Other Means of Promotion
You could try to promote your video on social media. You need to continue exploring other ways of creating viewership and engagement for your video. Depending on SEO alone is not enough.

For those of you interested in using YouTube as a platform for your videos, this next section is for you.
How to Rank #1 on YouTube?
Let’s say that you have an engaging video ready for YouTube. Let’s work on getting that video to rank higher.
YouTube Keyword Research
We discussed this earlier in this chapter. It is the first step towards ranking on YouTube.

Identify Search Intent
Search intent is a crucial factor in keyword research. It refers to the context and the reason behind a user’s query.
YouTube search results can help you identify this search intent.
Establish how your video addresses different users’ intent. If your video is a tutorial, YouTube likes step-by-step guides. If your video ranks different items in a specific category, use a listicle format.


High-Retention Videos
You are now familiar with the concept of audience retention.

Let’s look at the steps that help to optimize audience retention in more detail:
You may have decided what your video is about, but you still need to flesh out a proper plan before producing it. If it helps, write down the script for your narration. You can also create a storyboard for it.
You have come across this step before. The first 10 to 15 seconds of your video are crucial. These few seconds set the tone for your video and help viewers determine whether they will watch your video to the end or not.

To increase user engagement, ask people to comment, like, share, or subscribe to your channel in every video.
If your video is lengthy, you need to edit it strategically. People do not like to sit and watch monotonous videos. They want to watch videos that they find engaging.

These editing techniques can help you increase retention:
- Add jump cuts to quickly transition from one scene to another.
- Minimize gaps between key scenes.
- Guide your viewers to the video elements you want them to focus on.
- Use stories or narratives to share information.
- Feedback is important
Feedback is not limited to viewers leaving comments on your videos. The feedback process begins with your video SEO team. You should use them to:
- Get feedback on your script.
- Get feedback on your video edits.
An engaging video is a result of actively soliciting and getting feedback even before you release your video online.
On-Page Video Optimization
This step refers to all the tweaks and changes you need to make to your on-page video elements.

A few basic reminders:
- Craft an appropriate title and description.
- Choose or come up with an engaging and relevant thumbnail.
- Use tags whenever necessary.
Optimizing In-Video Elements
Your video has elements that need optimizing. For instance:
- Include video transcripts (This was previously mentioned in optimizing the search section).


YouTube cards are an interactive feature that is displayed towards the end of videos. It allows the video content producers to share clickable links to other content that they believe viewers might be interested in. By utilizing YouTube cards, you allow your viewers to:
- Watch other videos you’ve chosen for them
- Browse through another YouTube channel
- Donate to nonprofit organizations
- Answer a poll-type question
- Click on an external link
You can add these cards by linking them to your video timeline. When the viewer reaches that part of the video where you linked a Youtube card, it appears on their screen.
YouTube end screens are similar to YouTube cards. The only difference is that YouTube end screens only become visible towards the last 5 to 20 seconds of your video.
Publishing and Promoting Videos
The first 48 hours after publishing your video are important as they can tell you how well your video did. Of course, you should use these 48 hours to promote your work. Here are a few factors that you should consider during this crucial time frame:
- Determine the best time to publish your video.
What time are your targeted viewers on YouTube? When are they most likely to click on your video? Finding the best time to publish your video is one of the most crucial factors that will help you gain a higher viewership for your work.
Though there is no exact formula for the best time, you can try monitoring YouTube’s peak viewing hours.
Engaging with your audience is key to promoting your video. YouTube offers you a way to like comments, and reply to them. Use this feature to your benefit.
- Leverage your existing audience.
You can try to gain new viewers for your channel or videos, but don’t forget about the audience you already have. One way to boost views from people who have watched your videos before is to promote your video on social media.
You can send out newsletters whenever you have new content.

- Include links on your social media handles.
Make your video links more accessible on social media by publishing these links alongside your social media handle.
- Promote your videos to new audiences.
If you do not have an existing audience, promotion can be tricky, but there are ways to gain new audiences:
- Look for relevant discussion boards like Quora where you can share your video links.
- Try collaborating with other YouTube channels.
- Pay for YouTube ads based on your targeted keywords.
Optimizing New Videos
After publishing a video, you can no longer edit it, but you can use the data you have from your existing videos to optimize subsequent videos.

- Analyze your audience retention graph on YouTube to get to know what your viewers like.

- Find out if your video aligns with the search intent of your viewers. (You can do this through your YouTube studio dashboard)

Now that you know the steps you need to perform to rank on YouTube, let’s turn our attention to getting your videos to rank on Google.
Rank YouTube Videos on Google
There are several steps you can follow to get your YouTube videos to rank on Google.
Look for Potential Topics
As you read in an earlier chapter, topics that might rank on YouTube might not rank on Google. Your priority now should be topics that people search for on Google.


You can also focus on the video intent behind a topic. For instance, when looking for instructions on how to cut up certain fruits, people are more likely to watch an instructional video than try to read about it. Knowing this, you need to do some research on appropriate video keywords that are relevant to your chosen topic.
Optimizing Your Video for Suggested Clips
Google uses suggested clips to feature highlights from selected videos that it believes to be relevant to a search. They are embedded in SERPs and play directly from them. Users can therefore preview parts of a video through suggested clips.
To increase the chances of your video becoming one of these suggested clips, you need to make sure that your video is concise, helpful, and engaging.

How to do this? If your video is a step-by-step tutorial, you need simple action words for each step. For example, if your video is about making lemonade, your video’s instructions can be:
“Squeeze some lemon juice into a glass. Add sugar and salt according to taste. Mix it well using a spoon. Pour ice cubes into the glass. Fill the glass with water. Finally, add a mint leaf garnish.”
What we are trying to show in the above example is the significance of simple action words. Do not add unnecessary content to your video. Use a clear voice for narration.
Lastly, if you provide instructions for something, make sure that the accompanying video clearly illustrates your point. For example, if your video says pour ice cubes into the glass, show ice cubes being poured into a glass to support it.
These techniques will aid your video’s chances of becoming a suggested clip for a relevant query when performed successfully.
Take Control of Your Closed Captions
It is unattractive to have incorrectly closed captions in a video. YouTube adds these automatically to your video, and they can be full of errors sometimes.

Add in your captions to ensure that they are correct. This will help with user engagement and your Google ranking.
Use A Compelling Thumbnail
The thumbnail image you choose should make viewers want to open your video link. Make sure to use a thumbnail image relevant to your video so that people searching for the content you offer can easily find it. A compelling thumbnail needs to be:
- Customized based on content
- Appropriately sized. Your image should not appear stretched or pixellated. It should be the right aspect ratio. (Google’s aspect ratio is 16:9.)

- If your video content solves a problem, your image can show that problem being solved.

- The Thumbnail images are small. Make sure your audiences can easily see what they contain. If there is any text, it should be readable. Use contrasting colors to make any elements in your graphic easy to see and make out.

- Add descriptive text in the video description field to go with your thumbnail image.

Highlight Key Moments From Your Video
Google has a relatively new feature that allows users to survey important moments from your videos through time stamps. The feature is called Google Key Moments. It allows users to skip to a specific section of your video that they find relevant. Since it gives videos more chances to rank, you should consider taking advantage of this by adding timestamps to your videos.

Fundamentally, this entails creating an outline of your video based on timestamps in YouTube’s video description box.

The basic elements for creating Google Moments are:
- Timestamps – This is a link to a section of a YouTube video. It is usually in the following format: [hh] : [mm]:[ss].
- Labels – These are one-line descriptions of the clip.
Make the most out of your timestamps by doing the following:
- Use the video description box for your timestamps. Do not put them in a comment.
- Every timestamp should be entered on a new line. Do not enter them all in a single line as this looks cluttered and can be confusing for viewers.
- Aim for concise and descriptive one-line labels.
- Follow a chronological order for placing your timestamps.
- Avoid adding too many timestamps for one video.
Please note that the Google Key Moments feature only works with content from YouTube at the moment.
In these modern times, every smartphone is equipped with a video camera. Videos are as popular as ever. They have become more accessible and easier to make.
However, creating effective, relevant, and engaging videos is still an intangible skill that is hard to quantify. Despite the absence of a holy grail for creating the next viral video, we hope that you can use the ideas and techniques presented in this chapter to make video SEO work for you.

by MYB Agency | Jun 22, 2021 | Digital Marketing
Chapter 6 – International SEO
What Is International SEO?
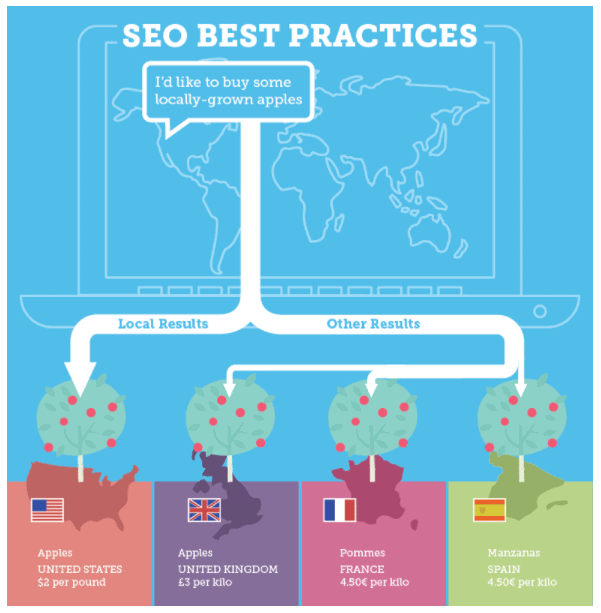
In the previous chapter, you learned about local SEO and how it can uniquely benefit businesses whose potential customers are located within a certain vicinity or area. In this chapter, we shift our focus to international SEO. But wait, what does international SEO mean?
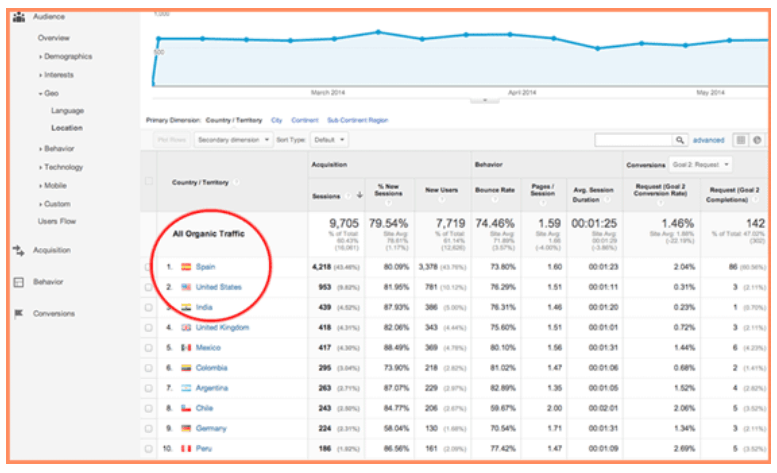
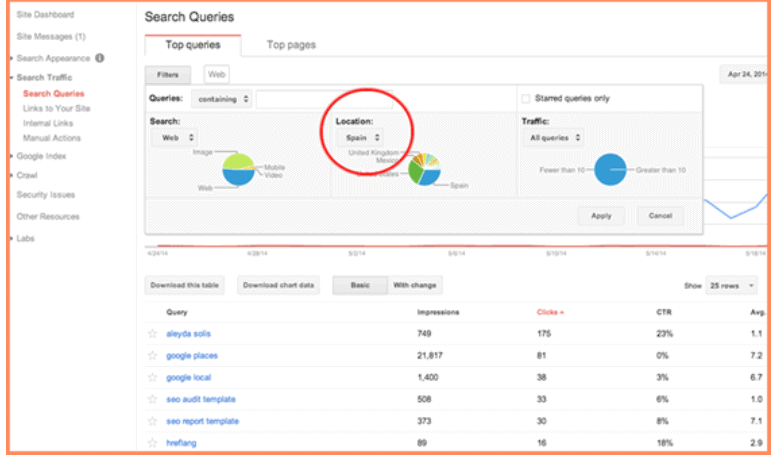
International SEO refers to the optimization process that helps Google or any other search engine recognize the countries you want to target through your business. It also helps the search engines identify the languages you utilize for your business. While local SEO might target certain neighbourhoods or even cities, international SEO is generally directed towards websites that wish to cover a much larger geographical scope such as certain countries or regions around the world.

Why Does Your Website Need To Go International?
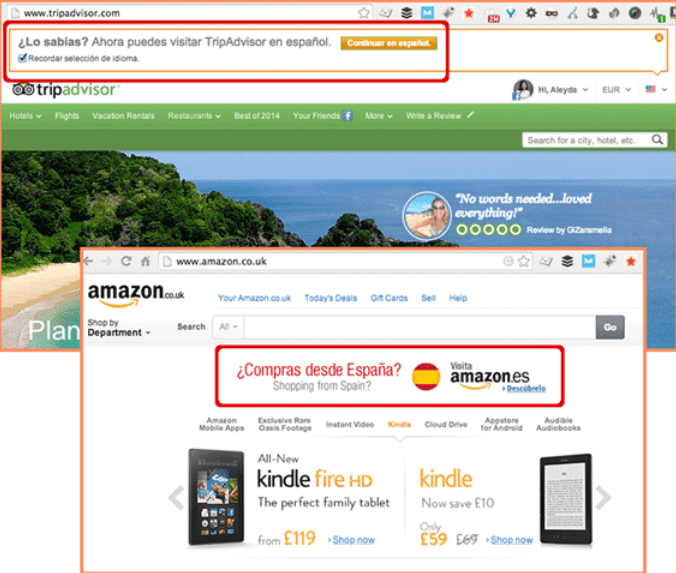
If your business website deals with international visitors, you must optimize your website to anticipate the needs of the different audiences that you are targeting. For example, a company selling its products in both the United States and Spain will probably have significant differences in the way it presents itself depending on the location of the visitor. An American visitor may view the website in English while someone from Spain may see a version of the same website written in Spanish.
What elements for international visitors must you focus on? Language is just one of the many components that can be adjusted to make international SEO work for you.
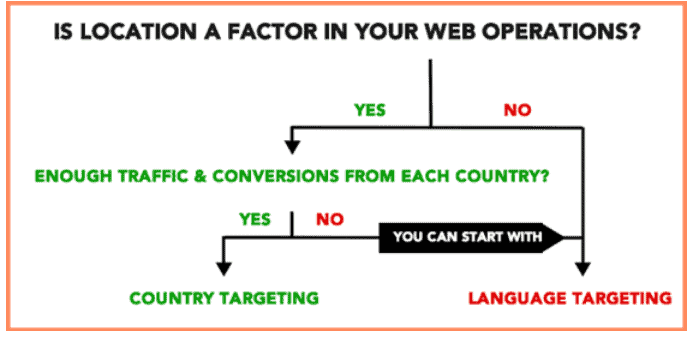
If your website caters to different countries or regions around the world and you have decided that international SEO is for you, here are a few general guidelines to look into:
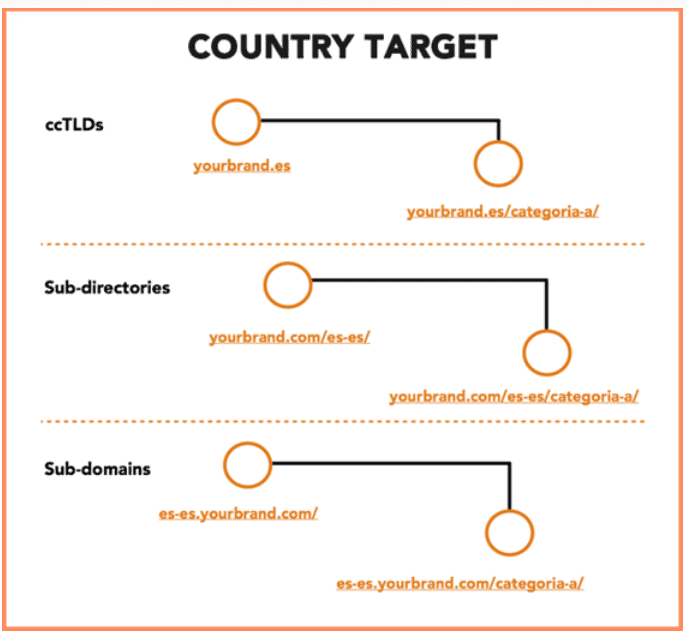
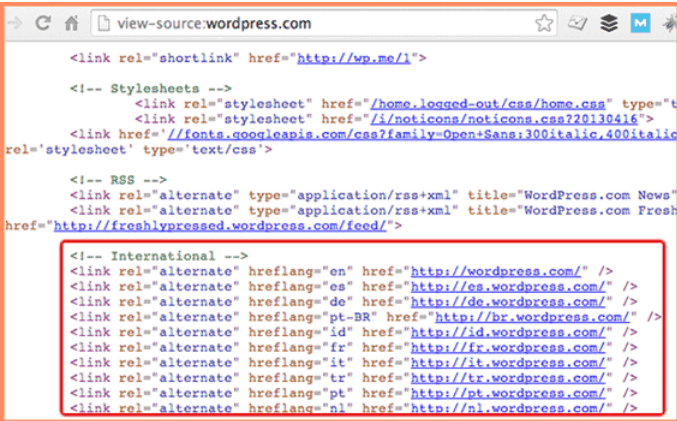
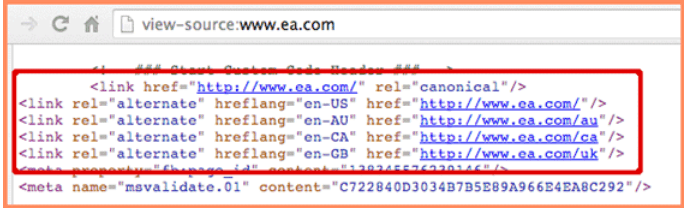
- Your website must state the countries you want to target (also known as country targeting). This requires URLs that are internationally friendly which entails adding country codes in your URL, e.g., “us” for the United States, “jp” for Japan, “uk” for the United Kingdom, etc.
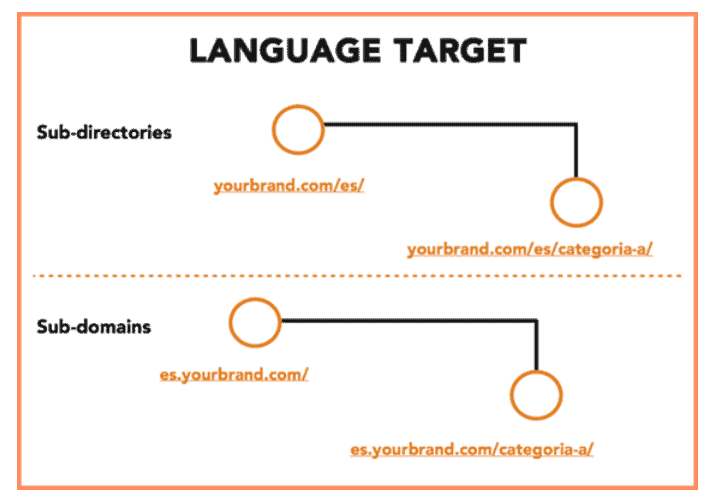
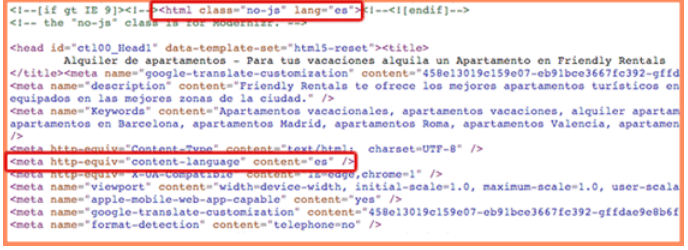
- Your website must state the languages you want to target (also known as language targeting).
- You must remember to generate content using the targeted language as it not only helps you in your ranking, but also helps with user engagement.
Some websites deal with a particular country or a language. If you plan on something similar, your targeting goals are less. E.g., if you have an online book publishing company specifically for the Spanish language, Spain is not the only country for its sales. Hence, your target must be the language and not the region.
After outlining for you the three basic requirements for launching a website that employs international SEO, let us now move on to a more thorough checklist of considerations for you to use.
International SEO Checklist:
You can refer to this checklist to see where you rank on the international SEO process. Don’t worry if you don’t understand every item on this list. We will discuss them further in the section that follows.
Research Section – Check Your International SEO Potential
To determine if your website can develop a presence, look into your:
- Current website traffic
- From other countries
- From other languages
- Recent organic search visibility
- Keyword results in the shortlisted countries and languages
If your SEO meets the criteria in the Research Section, proceed to the next checklist.
Targeting Section – Target Your International Web Visitors
- What to target
- Country / language targeting
- Behavioral patterns / characteristics of international visitors
- International competitors
Once the first two sections are complete (i.e., Research Section and Targeting Section), you’re ready to move on to the next steps.
Optimize Section – Develop an Internationally Targeted Site
- Choose a web structure
- Localize your website
- Navigation through your chosen web structure
- Hreflang/ Canonical tags
- Promotion within international community
- Geolocation
- Local IP address
After finishing the Optimize Section, proceed to measure your progress.
Measure Your International SEO Process
- Did you track each web version independently?
- Did you perform a follow-up with international search visibility?
This checklist answers your questions regarding your international SEO process. Now let us see the fundamentals (Research, Target, and Optimize) in detail.
The Fundamentals of the International SEO Process
You must know the fundamental elements of the international SEO process. They help you prepare your plan of action.
There are three primary phases to begin your international SEO process: research, targeting, and optimization. Let’s get started.
Research
The international SEO process requires extensive research in the beginning. This research helps you identify areas you need to work on for complete optimization.
Before we begin, ask yourself: What is the status of your current international organic search?
To answer the above question, you need the answers from our Research Section – Check Your International SEO Potential.
To learn more about your website traffic, search visibility, and keyword results in your chosen countries and/or languages, you can use the Google Analytics Tool. Refer to Geo reports which is below the Audience section.

You can also utilize Google Webmaster Tools to filter by location.

Finding the answers to these questions helps you formulate your strategy for international SEO optimization. If you know what countries and languages provide you traffic, you can customize your site to give international visitors from the same country or who speak the same language content based on their local behaviors, preferences, and culture.
When you perform this research, you might find out that your website already receives a reasonable amount of organic traffic. You can then focus on the existing traffic you have based on country or language for the optimization process.
If, however, your organic search traffic is low, you must find other international markets for your SEO process. This will entail more resources from you as you begin your international SEO efforts.
The next question you must ask yourself is: How much potential does your international organic search entail?
It is assessment time! Evaluate the potential of your targeted countries and languages of your website to answer the above question.
You require keyword research to fulfill this step.
- Find out what the relevant keywords and phrases are from your international visitors. These queries should be related to your business, products, or services you provide.
- What is the organic search volume for these keywords and phrases per country?
- How competitive are the keywords per country?
- What current rank do you hold for these keywords in the targeted markets?
The keywords that are already bringing organic traffic to your website can help you find other relevant keywords. How? By using tools like Ubersuggest, an SEO and keyword discovery tool. We recommend this tool because of how simple it is to use. You only have to enter your keyword in the search bar to receive a list of keyword ideas.

In addition to providing you with related keywords, Ubersuggest also gives you relevant information surrounding the existing competition for the keywords you are considering. It gives you information about keyword difficulty (how hard it is to rank in Google), cost per click (CPC), and paid difficulty (the level of difficulty you’ll have to face if you were to run a campaign with that keyword).
Once you have all this information, you must find out how your web pages rank by country.

For the optimization, you need native language support. It is necessary for keyword research.
When you use Google Translate, it is not always accurate. Words and sentences can have different contexts, and the literal translation may change their meaning. Similarly, if you want to use Google’s Market Finder for easy translation, it may mislead you. Occasional usage is not entirely wrong, but it should be relevant.
Once you complete the steps of finding the relevant keywords and finding out their organic search volume, it is time for you to establish the ranking difficulty for each keyword.
Moz Keyword Explorer is beneficial in terms of finding the competitive level of the keywords. There are other tools like Authority Labs or Unamo SEO that work as rank checkers.
By now, your research is complete. Let’s proceed to the next step: targeting.
Targeting
Your priority should be targeting countries based on their ability to generate organic search traffic for your website using relevant keywords.
If targeting a country is not yielding results, you can always target a specific language.
You must ask yourself: What would yield better results, targeting countries or certain languages? Only you can determine the answer as it depends on your company’s core nature. For example, companies like Walmart need to target the United States because of where their physical stores are. On the other hand, software companies like Atlassian, the developer behind an English project management software, needs to target all English language users.
This process maximizes your chances of receiving organic traffic and desired conversion rate. Once you achieve that, you can gain relevant visitors to your website based on your targeted audience.
There are different types of structures depending on the characteristics and restraints of your website.

Below is an overview of the different ways you might decide to target specific countries or languages.
Country Targeting
Chances are, you’ve probably already experienced (and can probably already guess) how specific countries are targeted by different websites. You may have noticed that websites in your country have a common two-letter code. This is how webmasters use URLs to target different countries. There are, however, a few different ways to integrate them into URLs. They each affect how your website is structured and comes its own drawbacks and benefits:
- Country Code Top-Level Domain (ccTLDs)
This structure for country targeting is beneficial as it provides a specific country extension, but it requires more effort to increase the domain’s popularity as it starts out as new and independent. This is ideal for large multinational companies who have the resources to acquire a domain and build it up from scratch.
Example: https://comprehensiveseoguide.us
Google treats some ccTLDs as generic top-level domains (gTLDs) which are not associated with any country code. A generic top-level domain refers to the kind of website. For example, websites with “.org” in their URLs generally refer to nonprofit organizations, website URLs with “.info” are generally used for information-driven websites, etc.
ccTLD is a desirable web structure, and companies like Tripadvisor and Amazon use it.
Subdomains are a great option if you have gTLD, but do not want a complicated structure. When you need to index a large amount of content, you must separate different web versions into sub-directories.
Example: https://us.comprehensiveseoguide.com
On the down side, Google recognizes each URL as a different domain and you will need to build up SEO for each. Though it is much less complicated in structure, this option entails a lot of effort in increasing every individual subdomains’ popularity.
Companies like Shop and Beats by Dre use this structure for country targeting.
You can get profitable results if you use this structure along with gTLD. In terms of implementation, this is the easiest as it is just another folder on your site. You also have the advantage of inheriting all the ranking from your root domain
Example: https://comprehensiveseoguide.com/us
Companies like Spotify and Electronic Arts use this structure for country targeting.

Language Targeting
Language targeting relies on Google’s machine learning algorithm to detect the language/s a user knows. Similar to country targeting, it makes use of the URL structure to integrate language codes that determine the language in which a web page should be displayed.
The structure you choose to implement for language targeting is, in principle, the same as the one we just covered for country targeting. Different language websites separated by subdomains are interpreted by Google as individual domains for which you will need to build up optimization from scratch. Subdirectories, in contrast, will share the same SEO equity as your root site.
- Language targeting by subdirectories are used by companies like Skype and Atlassian. URLs that employ this structure typically look like this: https://www.comprehensiveseoguide.com/en
- Language targeting by subdomains are used by companies like Wix and WordPress. Sites that employ this method have URLs like this: https://www.en.comprehensiveseoguide.com

When you select one of the alternatives as your website structure, make sure you are consistent in the structure you choose. Overlapping these alternatives will result in complications.
Once you finish research and choose your targeting structure, it is time to optimize.
Optimization
Optimization is fundamental as it makes your website crawlable, indexable, and relevant. It also helps in sending out properly targeted signals to avoid any issues with search results.
Let us look at some general international web optimization elements:
Different web versions need to be crawlable and indexable. It requires independent URLs following the relevant web structure you choose. It is not wise to use scripts or cookies as they make indexing difficult for search engines. If you are using different web versions, make sure that they are linked together.
If you have many web versions, you can only link the main page to the most popular one and you should feature all the web versions on one internal page.
Translation or localization (by language or country respectively) of different components is crucial for every international web version. You can do it using the keywords and phrases you acquired in the research. The elements you can work on are:
URLs, Title and Meta Descriptions, Menu and Navigations, Headings, Images and Alt Descriptions, Core Content, Reviews, among others.

Some websites have titles and URLs in English, but other elements of the page are in another language. This inconsistency confuses users and makes your page irrelevant to search engines.
Your international visitors might have questions about your content. It is a good practice to answer them when translating other components. This practice increases the credibility of your website.
- Automatic Detection of Language or Country:
If you want to know the country from where your international user is visiting your website, you can check their IP address. If you want to know their language, there are options available on the browser. You can conduct this research to redirect the users to the correct web version.
When looking to introduce language or geographic customizations:
- Make sure not to use pop-ups to learn more about your audience as they can be too obtrusive.
- Be careful when asking for information from visitors or making suggestions in your site. Visitors may not always understand the context of your questions or may feel intruded upon by sudden and unwarranted suggestions.
- Ensure that all your web versions are crawlable.

You need to display the character encoding of your page, specifically when you handle non-ASCII characters. ASCII characters stand for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. It refers to the characters you can find on a traditional English keyboard (Alphabets A-Z, Numbers 0-9, and punctuations). Non-ASCII characters are characters that are not in the English language.
You can specify the language in which your web page should be displayed in several ways:
- HTML Lang, Content-Language Meta Tags, and HTTP Headers
HTML language attributes and meta-tags are ways to identify language by search engines like Bing. You must set the right annotation within the html tag and add the correct language code.
Google does not utilize these attributes as it depends on its own algorithm in matching different target audiences with different versions of a website.

- Language Specification by Hreflang
Hreflang annotations are essential for search engines like Google. They identify the language used in your webpages and enable Google to serve that language version to users who are performing a search in that same language. Here are some things to remember about the hreflang attribute:
- The simplest way to use hreflang is by including it as an HTML link in each page header.
- Specify it as an HTTP header for non-HTML files.
- If there are many web versions, you can add them in the XML sitemaps. (An XML Sitemap refers to a file that contains the list of URLs for a website)
You can use Hreflang with canonical tags. Canonical tags tell search engines which URL is the official version of a page.
There are tools like flang that work as a validator for the implemented annotations. You can also use SEO crawler tools like Rob Hammond to check many pages at once.

If your plan includes targeting countries, you need to geo target your international web versions apart from specifying the language. To do this, you can use:
- Country Specification by Hreflang
Hreflang is not only useful for specifying the language version that search engines should serve to specific users, but is also useful in targeting specific countries. Hreflang gives you the ability to target people speaking a certain language in certain countries.
For example, the English language is used the world over, but by using the hreflang tag, you can target English speakers in the United States and the UK. There are also instances when you may be targeting English speakers, but would like to serve English speakers in the United States a different version of your web page than English speakers in the UK. Tweaking your hreflang attribute allows you to do either of these things.
In writing out your hreflang instructions, remember to include language codes as adding only country codes will not work.

- Geolocation through Webmaster Tools
Webmaster tools are particularly useful for websites that utilize sub-directories or subdomains in their website structure.
However, this is not the case for websites utilizing a country code top-level domain (ccTLD) structure. For ccTLDs, use instead the Google Webmaster Tools, Bing Webmaster Tools, or Yandex Webmaster Tools.

Maintaining a static IP location for your website used to be important for reasons of stability and simplicity. Websites with a static location were easier to find and more compatible with different operating systems. Times have changed, however, as search engines can now get more accurate geolocation signals by using ccTLDs or webmaster tools.
Now that you have a clear idea of the fundamentals of international SEO, let’s take a deeper look at how international SEO is different from regular SEO.
How Is International SEO Different from Regular SEO?
If your home country’s website is similar to the international web version of your website, it will not attract traffic. You need to localize the international web version to match the targeted country’s local audience to help improve user experience and make your international version more crawlable.
The fundamental difference between regular SEO and international SEO is regular SEO does not involve unique approaches or web versions for different countries. That is what changes in the international SEO process. Regular SEO focuses on a broader means of ranking, but an in-depth international SEO process focuses more on details like country and language targeting. International SEO is also more focused on helping a website rank in the targeted country using the appropriate web version of the website.
Let’s delve into the advantages of a multilingual website.
How Does a Multilingual Website Help?
If you want your international web versions to rank, you need to work on growing its multilingual features. Google tries to personalize user experience as much as it can, and in doing so, it not only answers queries based on your location but also your language.
There are websites like Kinsta who saw an 18 percent boost in organic traffic by translating their content into ten different languages.
Another reason why a multilingual website helps is it offers a better user experience. Your efforts in the multilingual website help your conversion rates.
But what do you prioritize in building a multilingual website? The answer is international keyword research. Let’s look at the steps involved.
International Keyword Research
By now, you know why a multilingual website helps your international SEO process.
It is important to note, however, that you need professional translators because they understand the culture and the background of the targeted language. Once you are clear about this, there are several steps to perform international keyword research:
Keywords List
You know how to do this step from the research part of the fundamentals of international SEO. Hence, keep this list of keywords ready.
Translation
It is time for you to translate these keywords into your targeted language. As a bonus, try translating all the relevant keywords and phrases which you believe are related to the original keywords.
Analyze
To maximize your efforts, try analyzing your keywords. As mentioned above, you can use Ubersuggest for analyzing which keywords will be beneficial for you.
There might be several keywords that may generate organic traffic, but do not help with conversion. Analyze them to avoid wasting your efforts on useless keywords.
Competitor’s Focus
Once you have your keyword list, you need to know what keywords your competitors are using to generate organic traffic for their sites.
Tools like SEMrush’s Domain VS Domain help you identify these keywords. Before you use these keywords, remember to analyze them.
Organizing Your Content
It is time to optimize your content. You have your keywords list, and now you need to use them in a proper context. This is where you employ professional translators to help you deal with other languages.
Track Your Keyword Success
Once you make your web version public with your keywords, you must track how each keyword performs. This step helps you to further the optimization process.
Now let us move on to the targeting signals you can use for international SEO.
What Are the Technical Signals for International SEO?
Technical signals help your website become more crawlable and indexable. The more technical signals you send, the easier it becomes for search engines to identify your targeted countries and languages.
Hreflang Tags
We mentioned hreflang tags before in the optimized part of the fundamentals of international SEO. To refresh your memory, an Hreflang tag works by optimizing your URL to help specify the language you want to target. By now, you also know that tools like flang Hreflang can help you generate these tags.
X Default Tag
xDefault tag is beneficial when you do not have the required language version of your user’s website, but you want to direct them to your preferred version.
Meta-Content Language Tags
Meta-content language tags help search engines identify your HTML content’s language, however, they are not as specific nor as customizable as hreflang tags.
Using Schema Markup
As mentioned in chapter 4, How to Rank: A Blueprint, schema helps search engines identify useful information for users. You can use schema as a technical signal for international SEO also.
You may use the Google Tag Manager to use schema as a technical signal. Since it is also a ranking factor for Google, it also works in optimizing your website.
Let us move on to geotargeting.
Geotargeting
Geotargeting is the process of delivering differentiated content to visitors based on their geolocation. This becomes your priority once you have put into place all the relevant technical signals for your site. You can assess your website’s performance using Google Analytics. Use Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to identify possible issues with your website as well as to learn its geotargeting potential.
Search Console:
You need to decide on your web structure before you begin the geotargeting process. For instance, if you decide to use ccTLD as your web structure, you can add them to the search console and use the relevant functions based on your ccTLD structure.
You also need to check that your hreflang tags are appropriate and working. Do this by:

- Ensuring that your country-targeting is correct (If you select ccTLDs as your web structure, it will automatically detect your targeted country).

- Performing the same steps on Bing Webmaster Tools.

Now that we have geotargeting in place, let’s learn more about how link-building works for international SEO.
Link-Building for International SEO
Building links is a crucial part of your international SEO process. If you are using ccTLDs or sub-domains as your web structure, you will need it all the more.
Why do you need link-building? Link building is essential as it builds the website’s domain authority and attracts relevant organic traffic. It also helps to improve the website’s searchability. For link building, you need to remember:
- You require a local citation builder.
- You need to do thorough research about your competitors. Once you have information about your competitors, look for websites and influencers you can build a relationship with to help promote your website.
- Utilize tools like BuzzSumo to find trending topics that are relevant to your website.

- You cannot have repetitive content as it does not help with your link-building process. If your content is optimized, you will earn quality links for your website.
- Employ unique strategies in planning for multiple countries. Do not oversimplify the process by using the same method for all regions.
Before we close this chapter, let us look at some tools you can use for the international SEO process.
Tools for International SEO
There are several tools that can help with international SEO. These tools have different functions and can be segregated into categories:
For Researching
- Google Webmaster Tools. Search Queries helps determine your visibility in international searches.

- Google Analytics. Its demographics section can help you understand your current traffic and conversion rate.

- SearchMetrics. It helps you identify your current position relative to your competitors.
- UberSuggest. It helps you identify keywords.

For Targeting
- Google Consumer Barometer. It helps you identify the characteristics of your targeted country or language.

- SimilarWeb. It helps you to understand your competitor’s characteristics and behaviors.

For Optimizing
- DejanSEO Hreflang Validator. It helps you implement the correct hreflang annotations.

- Google Webmaster Tools Geolocation Feature. It helps you geolocate your website if you are targeting a specific country.
- TwitterFall. It helps you follow up on your topics and also helps in geolocation.

For Promoting
- Open Site Explorer. It helps you understand your competitor’s strategies, sources, and popularity.
- Link Prospector. It helps you promote your website through various factors.
For Measuring
- I Search From. It allows you to simulate a Google search from a different location or device. You can also customize search settings.

- Moz Rank Tracker. It helps you monitor the ranking for each of your web versions.
If you are in charge of an enterprise that is seeking to gain ground in a region, country, set of countries, or perhaps people who speak a certain language, then you will need to make international SEO and its general principles work for you. We hope that this chapter provides you with the foundation you need to do just that.

by MYB Agency | Jun 22, 2021 | SEO Training
Chapter 4 – Local SEO
What Is Local SEO?
When was the last time you looked to have food or grocery delivered to your doorstep? How often do you turn to the internet to look for an address of a company you want to do business with? When you do either of these things you are relying on the power of local SEO.
Business owners who have a brick-and-mortar shop or serve a particular geographic area leverage on local SEO to increase traffic and brand awareness. There are various tasks associated with local SEO. Some of them include searching for local keywords and creating a Google My Business account. Local SEO utilizes NAP citations which stands for name, address, and the phone number of the company. This citation also includes a link to the company’s website.
Why Does Local SEO Matter?
According to Google, nearly 46% of all its searches are for local companies while 76% of users who perform a local search on their phone visit a local business on the same day. Since results for local SEO usually include operating hours and reviews from other consumers, you can imagine what an impact it can have on a company’s revenue.
Inarguably, local SEO matters for businesses that need to thrive at a local level. NAP citations built through local SEO can help a local business’ Google ranking as long as the information is accurate and relevant.
In 2016, Google began including a small yet significant update to the way that search results, particularly for local businesses, appeared. Referred to as a local pack, it points to the expandable section towards the top of SERPs when a user submits a query that Google interprets as local SEO.
Since then, NAP citations have grown and become more accurate, businesses have learned to use Google My Business, and local SEO has grown in use and popularity.
The question now is: how can you leverage on local SEO?
How to Optimize Your Website for Local SEO
Think about it: If your website is not optimized, how can local SEO alone help in Google ranking?
The short answer is: it cannot help. You can have local SEO without optimization, but you would be missing out on a significant opportunity to have a higher ranking on Google without it. Hence, website optimization needs to happen before you begin local SEO efforts.
Significance of a Proper Contact Page
Your website needs a committed contact page. Users want to know more about your company before deciding whether or not to do business with you. This is where the NAP citation is essential.
Double-check your name, address, and phone number on your contact page. Incorrect information is not only annoying for users, but can also keep potential customers away.

Add Business Addresses
If your company has more than ten locations, you do not need to add all of them, but if it has less than ten, make sure you add all the details for each address in a convenient place on the website. Usually, the business address is located in the footer section of a web page.
Link Mobile Numbers
People tend to use their mobile phones when looking for local business. Hence, it is crucial to make all the mobile numbers listed on your website clickable. Doing so allows people to directly call your business without having to switch applications to dial your number.
If you don’t know how to do this, there are several websites which can walk you through the process.
Location Optimization
On many occasions, users are unable to locate or understand your business address. This is a frustrating experience for would-be customers and can lead them to find another business similar to yours that is easier to locate.
To avoid this situation, add a map or provide a link to your location on the website.

Testimonials Help
When you add testimonials to your website, it lends an authentic voice to your page and sends a positive signal to users and search engines. It allows prospective customers to survey your business beforehand and decide whether or not to pursue a relationship with your company.

Schema to the Rescue!
In the previous chapter, you came across the concept of schema markup. To recap:
Schema refers to particular code on your website allowing search engines to understand what your website is all about.
When you add a specific schema that clarifies that your website is a local business and not a major brand, you attract more local users.
There are tools like Hall Analysis that help you create schema for your website.

Now that you know how to optimize your website for local SEO, you need to understand how local SEO and search engines interact with each other.
Understanding Local SEO and Search Engines
As mentioned above, there are two concepts you should know: local intent and local pack. In this section, let us focus on local intent.
Do you notice when your geolocation is active, and then you search for a bookstore or a diner on Google, it gives you a result peppered with nearby places? It happens because Google senses local intent from you and reacts accordingly by displaying local businesses.
Since geolocation relies on either GPS technology or your IP address, you can end up performing a local search even when your geolocation is turned off. A search, for example, for “diners near me” will make Google list all the local restaurants near you.
Over the years, Google has simplified local searches for users by adding features to local SEO. The local finder is one such example whereby users can view a longer list of businesses than the initial three listed by the local pack.

So how does Google’s algorithm work when it comes to local searches?
Within the context of search engines, an algorithm is a series of instructions that a computer follows to produce an SERP in response to a query. However, when it comes to local SEO, Google’s algorithm works differently. Apart from the usual factors, Google considers other aspects such as:
- The relevance of the business
- Prominence and credibility of the website
- Proximity of the business to the user

Again, because of Google’s modified local SEO algorithm, it becomes really important to ensure that the information on your website (particularly your business name, address, and phone number) are correct and kept updated.
Understanding Local SEO and SERPs
When you look up information that Google recognizes as a local search, Google displays local search engine results pages or local SERPs. After performing local SEO searches for different things, you will notice that these results are displayed in the same format. However, there can be slight differences in format depending on whether the website has a local pack or is organically localized.
But wait, what is the difference between a local pack and a local organic search?
A local pack is what appears on an SERP when the search engine detects a local search from a user. Since it is based on location, Google typically shows a map of three business listings based on a location. An organic search is not based on location and the results can be a variety of different businesses, social media pages, news stories, blogs, videos, etc.
Local business owners should ideally aim to rank high on Google’s SERP and local pack listings. Below is an example of a local pack. Notice how the elements and layout are different from a regular search result.

Google identifies these local packs from the Google My Business account. It is a crucial part of local SEO marketing.
Having said that, let’s move on to how to make Google My Business work for you.
Local SEO Tips
Let us reiterate: your first step should always be to optimize your website before moving on to work on local SEO. Once you’ve done that, look into the tips below to build up your local SEO.
Create Online Profiles – (Principally Google My Business)
If you have a business, there are other ways to achieve an online presence apart from your company website. Consider platforms like Yelp, Tripadvisor, Facebook, and most importantly, Google My Business. You can also create your profile on local sites as it increases the chances for local reviews.
Why focus on Google My Business specifically?
When you create your profile on Google My Business, you are leveraging on Google’s local SEO feature and making it work for your company. Google My Business is invaluable because it allows you to enter and display details that are unique to local SEO such as your operating hours, contact information, and a link to your website. It also allows you to add your business location using Google Maps, which can be extremely beneficial to your business.

Don’t overlook business listings, directories, and review sites.
Earlier, we recommended adding to your online presence using other online platforms. Here’s why: search engines may show results from Tripadvisor, Yelp, and other similar websites when users search for your business. Hence, it’s best to create a profile for your business on relevant platforms such as these.

Pay attention to your social presence.
When considering how else to augment your online presence, strongly consider social media platforms. When doing so, make sure that you are being consistent with the information that you are providing so that visitors will know that your profiles across these platforms refer to one and the same company.
Generate Local Content
A blog on your website is one of the best ways to generate local content. When you create a blog, make sure it is on your primary business domain and people visiting your website can see it. Blogs are especially helpful because they can help you achieve natural links, one of the best ways to increase your ranking.

A great way to increase value for your blog is to create content that is localized. Local content makes your content particularly relevant because it is specific to your business and the place where it is located. The question now is: how do you create localized content?
- Mention local places found in your business’ immediate vicinity (cities and neighborhood)
- Add local news
- Highlight local events by writing about them or, if possible, sponsoring them
- Consider including opinions from local experts relevant to your business
Are there things to avoid when trying to generate local content?
Certainly. Make sure to avoid the following:
- Avoid trying to overly sell your products or services using your blog. Such posts are generally unhelpful and do not help catch the user’s attention.
- When you create local content for your website, make sure you do not copy other website’s information. Be genuine and make your services and products stand out by making your messaging a unique and authentic representation of your brand.
- Avoid various approaches to your business. Strive to keep your website’s brand as consistent as possible wherever and whenever your company is mentioned online.
Focus on Backlinks
When you are generating content for local audiences, you also need inbound links or backlinks. Your relationship with other businesses helps you improve your efforts to gain inbound links. Begin by initiating some online interaction with complementary businesses where you see a mutually beneficial relationship. Try leaving useful comments on their blogs and add a link to your blog.
Another way to go about link building is performing a backlink audit of your competitors. A backlink audit refers to the research you can conduct on your competitor’s website to find out the links that are pointing to them.
There are tools like Ubersuggest that help in performing a backlink audit.

Pay Attention to Your Target Audience
Knowing your audience is no less important when you are looking to utilize local SEO. Do you know who your target audience is? It’s an important question that you need to consider even before you begin working on your website. Your products and services, your content and the way it is written, including the look and feel of your site need to cater to your target audience.
To have a local perspective on who your target audiences are, you may want to take a look at tools like Zip Code Lookup.

Significance of Local Reviews
Do you know how easy it is to dupe people in business? Actually, with the internet and savvy consumers, it’s becoming harder and harder. Over time, the internet has provided users with increasing resources to differentiate between a legitimate and illegitimate business. How you ask? Through local reviews of course.
When your local business is up and running, people will post reviews about it. These reviews can consist of compliments, feedback, or overall experience. People check these reviews and ratings before planning to deal with your business.

If your website or business profiles lack ratings, you may face difficulty in boosting your local SEO. As mentioned above, when you join Google My Business, you automatically enable reviews to be added to your local pack.
Reviews are continuously posted by clients and potential clients. It is crucial to remember that every comment counts. If you receive any negative reviews, which at some point every business does, reply to them professionally and courteously. Most websites include a feature that allows businesses to acknowledge and respond to reviews in-line.
That being said, Google reviews are one of the most vital local ranking factors. No wonder some businesses resort to asking customers to post reviews. As good an idea as it sounds, asking customers to leave positive reviews of your business is not a wise course of action at all. The best reviews are authentic and are generated organically as a result of a genuinely positive experience with your business.
Additionally, Google has become wise to manipulated rankings. Incentivizing positive reviews, for example, is against local SEO policies.

Everything about Citations
Citations, as mentioned above, are the contact details of your website even without an actual link to your website.
These citations are a crucial part of local SEO as they generate local signals for your brand. You need to refer to an actual physical address when building them. If your business has different locations, you can customize it, provided you are consistent with your brand name and messaging across all citations.

If you are using abbreviations, make sure it is acceptable. You can refer to Whitespark’s complete table. More on this later.
Let us look at some ways to build citations for your business.
Use local search engines
Google or other search engines like Bing use web crawlers to look for citations to update their indexes. To ensure that web crawlers find your citations, you need to focus on listing your business on Yelp, Hotfrog, or any other relevant local directories.
Use local blogs
As you read above, blogs are an essential tool for boosting local SEO. Blogs can also help to build citations. When you optimize your blog using high-quality content and relevant inbound links, search engines can effortlessly find your citations.
You should also find other relevant blogs for inbound links as they can add credibility to your local business.

Use local directories
Local directories are similar to local blogs. They increase your credibility as a business. Try using local directories that are edited by people. If you choose machine-edited ones, there are more chances of spam.
Begin your search for local directories journey by adding your business to Best of The Web’s regional directory.

After doing so, you can customize your directory search by filtering your list using the targeted city or state’s name.
Industry-specific directories or blogs
Industry-specific directories or blogs are another way to achieve citations. Look for blogs or directories that are focused on your industry and find a way to have a listing (if it is a directory) or be mentioned (if it is a blog). They may not always be local, but search engines count them as justifiable citations.
Porch is an example of an industry-specific directory. Its website connects homeowners with home improvement professionals across the United States.

Citations are undeniably an essential part of your business’ online presence. Make sure you have them wherever relevant and that they are consistent.
Other Local SEO Tips:
Now that we’ve covered the basics of local SEO, there are other aspects that we recommend you check off your list once you’ve done the above:
- Improve your internal linking structure to give your local SEO a boost. As you read in the off-page SEO chapter, taking care of how your internal pages are structured is vital for your website.
- Optimize your title tags, meta descriptions, URLs, titles, headers and content as necessary for local intent.
- Add a location page to your website. It is similar to a citation and can help users find your business easier.
- Make your website mobile-friendly as it helps in local searches. Users are more likely to search for a local business using their mobiles.
Now that you know how to optimize for local SEO, let us look at some useful tools you can use.
Top Local SEO Tools
Local SEO tools help boost your local ranking. Here are a couple which you may want to consider using:
Moz Local
- Boosts your local visibility by validating the information in your business listing
- Sends location details of your business to online directories to eliminate duplicate listings of your website
- Provides access to a dashboard where you can manage your listings
- Updates your status across the web as soon as you enhance your data
- Allows you to monitor your reviews

Best Feature:
Moz Local automatically synchronizes your Google My Business profile and updates your listings according to the changes you make on this profile.
Price: Ranges from $99/year to $249/year. (Depending on the package you choose)
BrightLocal
- You can use this tool for auditing citations and Google My Business profiles
- Generates legible SEO reports
- You can track the search rankings for targeted keywords
- This tool can help fix and create new citations

Best Feature:
BrightLocal offers white-label reporting, which is a beneficial tool for business branding. In white-labeling, you add your brand to another company’s product to show an united front to your clients. The reporting tool allows you to customize your dashboard according to your needs..
Price: $29/month (single business) with a 14-day trial period
Semrush’s Listing Management Tool
- Employs Yext, a digital platform, for listing your business across all the social platforms
- Provides you with a dashboard to manage your listings
- Dashboard allows you to check the listing status of your website

Note: This tool is available only in the US, UK, Germany, France, and Australia for the time being.
Price: $119/month (with Listing Management Tool)
GrowthBar
- It is a Google extension, hence you do not need to leave the browser to check other details like backlink analysis, keywords, etcetera
- You can have detailed information for local keyword ranking
- This tool gives you information about your competitors’ keywords

Best Feature:
GrowthBar can help you identify the top-ranking keywords of your competitors.
Price: $29/month with a 5-day free trial
Whitespark
- This tool focuses more on local search marketing
- It helps in finding local citations, tracking ranks, and building your website’s reputation across all online platforms

Best Feature:
Whitespark helps you find promising links for optimizing your internal pages.
Price: $100/per location (You can add up to 5 industries or local sites)
Make Local SEO Work For You
Before local SEO, the local pack, NAP citations, and the tools mentioned above came along, small and local businesses had to rely on advertisements in local publications, printed phone directories, and flyers circulated in their neighborhoods. Today, business owners have a lot more control over how and where their products and services are promoted. If you are a business owner with a physical storefront or servicing a targeted area in your vicinity, make sure to take advantage of local SEO. It can help your business grow faster, more cost effectively, and efficiently

by MYB Agency | Jun 22, 2021 | SEO Training
Chapter 3 – Off-Page SEO
Now that you’ve understood the significance of on-page SEO and how it can impact your ranking and your business it’s time to look at another important aspect of SEO – Off-page SEO.
Why Does Off-Page SEO Matter?
Off-page, as the name suggests, refers to everything that falls outside the purview of the website. It refers to the tasks in which you have less or zero control. Whenever someone refers to off-page SEO, the only other term which comes to light is link building. But, while link building is an essential tactic, it is not the only one.
Off-page SEO is necessary for building the authority of the website. By optimizing brand building, content marketing, and your social media strategy, you can outrank other websites. Outranking other websites also gives you an idea about your competitors. And together, these tactics are useful for building a reliable reputation for your website.
Off-Page SEO VS Technical SEO
Off-page SEO is all about building a brand for your website. Therefore the tactics used here fall outside the scope of the website.
- Brand Building: It refers to the advertisements and campaigns that promote your business, brand, or company.
- Content Marketing: It refers to creative marketing strategies that do not directly promote your company; instead they provide a natural push towards your company’s services or products.
- Social Media: Social media links are a no-follow, i.e., it does not affect your ranking on search engines. But as an off-page SEO tactic, optimizing your company’s social media accounts might get you an organic audience which can positively affect your website’s ranking.
Technical SEO, on the other hand, caters to the technical aspects of the website like indexing and crawling. Several users confuse technical SEO with on-page and consider them to be the same. Though there are some similarities, certain components of technical SEO differentiate it from on-page SEO.
- Site Speed Optimization: It comes under the broader concept of web performance optimization. If your website loads quicker on a laptop and a mobile phone, it ranks better on search engines.
- Canonicalization: It refers to the process of adding canonical tags to your website. These tags are useful in marking specific URLs as prime copy of your content.
- Hreflang: It is an attribute that helps Google or any other search engine identify webpages in different languages on your website.
Now that you know the difference between off-page SEO and technical SEO, let us take a detailed look at the most important strategy of off-page SEO.
Everything About the Link Building Strategy
The link-building strategy ranks first in off-page SEO tactics as it serves as a root for all other tactics. Your aim when performing off-page SEO should be to build your website’s authority. For that, you need high-quality links from credible websites.
You also need to understand the attributes your website should have for effective link building.
How to Assemble a Page for Link Building?
Links are the most crucial factor for Google ranking. The initial steps for link building are vital since they are the foundation for off-page SEO.
Placing Your Internal Pages
Your priority in assembling a site page for link building should be optimizing your internal pages. Broken internal links do not bode well with users or search engines.
Categorization helps to boost a website’s performance. If you throw random internal links on your page (without laying them in a logical order), it will harm the website.
This is where the use of silo pages comes into the picture. What are silo pages, you ask?
Silo pages are static pages that categorize your content for Google to find topical relevance on your website. If your internal pages stand alone, it can disrupt the whole navigation process. Similar internal pages should ideally be linked together.
Remember, it is the quality of the links you provide that counts and not the quantity. Also emphasizing your brand name is crucial here.

Topically Relevant Elements
When it comes to relevance, it should cover both content and links. In the previous chapter, you came across the concept of keywords and how they are vital for on-page SEO.
It is necessary to mention here, how crucial on-page optimization is because very often website owners or site operators forget to pay attention to these details.
To find relevant keywords, prioritize identifying the core subject of your content. It will help you be aware of what people usually search for around your topic.

Another significant element is topically relevant links. When you search for high-quality links for your website, it is wise to look for thematically similar links. For e.g., if you have a website about cars, you should look for links from other car-related websites or blogs. That is how you make your links authoritative and relevant for the users.
Are you still finding it difficult to understand what authoritative and relevant links mean? Let us dive into the details of backlinking.
Backlinks: Ensuring it is Relevant, Authoritative, and Friendly
There are 3.5 billion Google searches all around the world every day. You read it right, 3.5 billion!
That is why off-page SEO optimization becomes more significant. Natural links play a crucial role in this optimization.
Wait, but do you know what natural links are? Other websites or blogs use your website’s link in their content as it might be relevant to them; those are natural links. These natural links increase the credibility of your content. It also helps to build relationships that boost your website ranking.
Google bot spiders continuously crawl and index new information on your website. Hence, the links you provide are essential. Earlier, the emphasis was more on the quantity of the links, not so much on the quality. But the focus today, by Google and other search engines is on user experience. If your website hosts broken links, it will reduce its chances to rank higher on search engine results pages. To avoid this, there are steps you can adopt to ensure your backlink’s optimization.
- Broken Link Building: This is a constructive step you can take for your backlink optimization process. Though Google does not bother about dead links, nor does it affect ranking, users may not find it appealing. Several users avoid websites that host dead or broken links. What you can do as part of the off-page SEO optimization process is to conduct thorough backlink research. The research will allow you to identify broken or dead links. You can then contact the owner of the website with the broken link and let them know about its status. If they find your information useful, they might add your website’s URL to their content.

- Significance of Infographics: Infographics help to display data in an appealing format. When you add relevant infographics to your website, it appeals to the users and helps in outreach, one of the strategies of off-page SEO. If you do not want to spend an extensive amount on designing these, you can always find websites that design them without burning a hole in your pocket.

Link Building Do’s and Don’ts – Things to Avoid
It is crucial to understand the do and don’ts of link building for the optimization process.
Do’s:
- Quality Content: If your website contains quality content, you’ve achieved more than 70% of the optimization process. It includes keyword research and adding value and relevance to your content.
- Backlinks: As mentioned above, backlinks increase the credibility of your website. It involves internal links as well as optimization of all broken or dead links.
- White Hat Tactics: It refers to everything you do to improve your website’s ranking ethically or as per rules and regulations. This helps maintain the ethics of your website.
- Patience: The link-building process takes patience and perseverance. If you imagine it happening overnight, you are mistaken.
Don’ts:
- Spam/low-quality engagement: It is always favorable for your website to engage in reputed and high-quality websites or blogs. Connecting with spammy links may hurt the website’s reputation.
- Specific anchor text: If you rely on a single anchor text, you miss the opportunity to diversify your content. Optimizing your anchor texts can help boost ranking. However, over-optimizing and breaking the rules may see you getting penalized by Google.
- Link exchange: It is wise to stay away from schemes that involve you exchanging your link for another. Remember that only specific and relevant links can help your website.
- Black Hat Tactics: It is the complete opposite of white hat tactics. It refers to practices that do not comply with the rules and regulations of the search engines. These practices are usually for improving website ranking.
Things to Avoid:
- Low-Quality Content
- Spending money for links
- Adding toxic links on your website
- No-index domains
- Irrelevant links
- Speedy link building practices
Do you know what happens when you do not follow these guidelines? Google can penalize your website. Let us look at some tips to avoid such penalties.
Checks to Avoid Unnatural Links and Google Penalties
Google’s primary focus is user optimization. As such it gives high value to websites that provide credible and relevant information to their users.
To avoid Google’s penalty radar, one should conduct thorough backlink research and understand how relevance works as a factor. There are some steps you can take to ensure Google does not penalize your website.
- Always remember, your content is for the users. Your website’s goal is to help users find relevant information or products. If your tone is overly promotional, it may become a reason for Google to penalize your website.
- Diversifying anchor text is crucial. As you read above, relying on one specific anchor text does not help your website. It just shows Google that you have too many unnatural links on one anchor text, and it does not bode well for your website.
- Add different but relevant keywords. Google does not appreciate keyword stuffing.
- Prioritize avoiding low-quality links. When you optimize your internal links on the website, users can navigate through your website with ease. Google notices these factors and gives your page a better ranking.
Now that you’ve understood everything about link-building, let’s look at another vital strategy. Do you know how Google decides whether a brand is authoritative and authentic? It is through brand signals. Let us look at brand signals and how they affect your website ranking.
Brand Signals Strategy: How to Generate them?
Brand signals help Google decide whether your website is a legit brand. It is, therefore, crucial to send the right brand signals as Google cannot differentiate between spam and legit brands. These are the ways to generate the proper brand signals for your website.
Inspect Brand Searches
Brand searches refer to the number of people who search for your brand on Google. It is advisable to audit and inspect these brand searches as they can provide valuable information about the kind of audience that visits your website.
You can find this detailed report on the Google Search Console. The columns of queries, clicks, and impressions give you the data you need to understand brand signals.

Use YouTube
Investing in YouTube is one of the smartest decisions in generating brand signals. It comes in handy, especially if you are considering video marketing. YouTube videos are known to get an audience for videos that ordinary websites cannot.
Using YouTube for marketing increases your reach and brand awareness as well as allows more people to reach your website.

Brand Tracking
Setting up brand tracking for your website will help you analyze how many people talk about your brand on different forums. It helps in understanding what enhancements your brand signaling needs based on user engagement.
There are tools like the Semrush Brand Monitoring tool that provide you detailed information, including brand trends about your website.

Add Studies and Research to the Content
Adding metrics, research, or studies to your content adds to its credibility. Not to forget the large number of high-quality backlinks it provides to your website.
Users come across these backlinks and use this credibility to share your website on social media. Though social media follows do not directly affect Google’s ranking, it has an indirect impact.

Now let us look at some other off-page SEO strategies you can use to increase your organic search traffic.
Other Off-Page SEO Strategies
There are several strategies you can adopt for your off-page SEO process.
Outreach as a Strategy
When you communicate and aim your content at publishers, you are using outreach as an off-page SEO strategy. It helps in boosting relationships as the principal goal of outreach is link building. Outreach uses the contributing factors of value, relevance, and creativity of the content.
Try Guest Posting
When you provide content for other websites or blogs, it is guest posting. It primarily helps in building quality backlinks and adds credibility to your website. It is crucial to understand the difference between direct selling and writing quality content. Guest bloggers often use the opportunity to advertise their services.
Social Media to the Rescue!
Your website needs an audience. User engagement catches Google’s eye, and it gives you a better ranking. And what better way to gather an audience than social media? Understand the power social media possesses in this generation, and use it for your benefit. You can optimize your social media game to the fullest by being attentive and responsive, following all the big but relevant brands, and maintaining a uniform online reputation.

The Power of Visual Representation
Do not underestimate the role of images and videos on a website. If a website contains lines and lines of information without any visual representation, it will lack appeal to the reader.
When you notice various kinds of visual information, like images, infographics, videos, or gifs on a website, it is not just for decorative purposes. It is also to catch the user’s attention and hook them to the website. It is also crucial to remember that all visual data should be relevant to the content you provide.


Be Attentive of the Web
Being aware of what is happening on the web is probably the most understated strategy for link building optimization. Following current trends and finding your relevance in them should be a regular practice. Communication with the users regarding these trends always helps boost user engagement on the website.
Build Relationships
Link building is all about building relationships. When you have healthy connections to other webmasters or bloggers, you can understand how outreach strategy works. Building relationships with other webmasters help your website reach audiences that you cannot.
Increase Trustworthiness
Credibility in your content can help increase your website’s trustworthiness. Trying to catch a user’s attention with attractive titles without any relevant content can harm the website’s reputation.
You may have noticed some websites with a lock beside the URL. That is called Secure Socket Layers or SSL. SSL allows the user’s data to be private and it is an effective way of building trust among users.

Be Open To Comments
If your website hosts a section for reviews or comments, you increase user engagement through interaction. But do not focus only on user engagement. Try and understand what these comments mean and what improvements they require. When you work on these enhancements by responding to their queries, you build a valuable reputation for your brand.
Make Use of Forums
Forums like Quora or Reddit get various kinds of audiences. The question and answer format of these forums help you talk about various aspects of your products or services with some indirect links to your brand.
Of course, it is vital to find relevant forums for your website. Haphazard links to your brand may seem too promotional, and users may mark it as spam.

PR, Not Marketing
PR refers to public relations. Though most people believe PR and Marketing to be the same, they are quite different. PR is all about building a brand. It is not about selling your content, product, or services; it is about selling your brand.
When you use PR as a strategy for off-page SEO, you are opening yourself to whole new avenues for content.

Use Podcasts
Podcasts refer to the audio files available online for users to download. It can be about any topic in a spoken form. Including podcasts, as a strategy can help with user engagement as 51% of Americans enjoy listening to them and it increases your audience. Again, understanding what podcasts will be relevant for your website is significant.

Pay Attention to Reviews
Reviews are a significant part of the off-page optimization process. The brand signals your website sends out creates its persona on the web.
Reviews from users for your website make a huge difference to your website. If they do not rate or critique, it means there is less user engagement.

To optimize your SEO strategy it is important to concentrate on all the factors that go into off-page SEO.